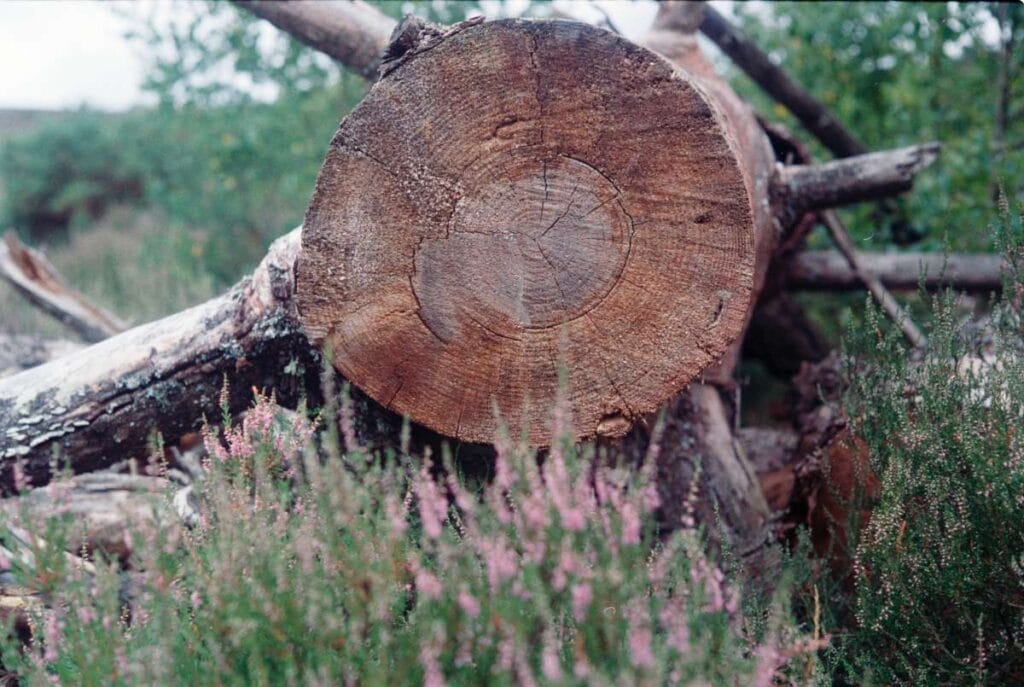
Natural decay turns logs into rich soil. Support timbers and beams, floor , ceiling joists, and roof decking can all be damaged by wood rot. The expense to replace rotten wood might easily run into the tens of thousands.
The most popular building material is wood, so understanding what caused lumber rot, how to stop it, and what you should do if you find it are all essential. Flooring, wallboard, even roofing can all hide wood rot. In case you were wondering, here's the skinny.
Distinctions exist between rotten and decaying.
The difference between "too late" and "salvageable" is that the former indicates hope while the latter suggests defeat. Despite being exposed to the elements, wood can be preserved.
Buildings typically have doors and roofs. Water is far more destructive to wood than either mould or rot.
For the wood fibres, this means abnormal growth and shrinkage.
The moisture content of wood is always one hundred when it is first cut down. The presence of water alters all conditions.
How can we restore wood that has been ruined by water?
Guidelines for rescuing rotten timber and a check list to establish whether or not the wood is deteriorating are provided.
Wood rots when moisture builds up in cracks but under paint and doesn't dry off. Unfortunately, once it begins, you will have to spend a lot of money fixing it or replacing it.
Rot in untreated wood threatens the integrity of the entire structure.
Termites love the wetness that comes with wood rot. Your home's wood components (the frame, the ply sheathing, the trim) require protection.
At Hitch Property Constructions, we offer timber repairs work from simple timber repair to almost new structures, renovations, and extensions.
What Causes Wood To Rot? Where Exactly Does It Lead?
Have you ever pondered the cycle of wood's growth, decline, and eventual demise? Feasts on wood and lives a humble existence. How? Read on!
The planet is teeming with animal and vegetable life. Sunlight is essential for plant life, including vegetables. All earth life would perish without their ability to absorb the sun's rays and convert them into usable nutrients.
However these definitions are oversimplified, it is safe to say that animals cannot absorb sun energy. While animals are free to roam, plants are firmly planted in one place. Mushrooms are rooted organisms that get their nutrients and energy from their food rather than the sun. Fungi were previously classified with plants, but in recent years, classification experts have opted to split the two groups apart. Plants and fungus are examples of "vegetable" life forms. Every living thing that doesn't acquire its food from the sun (that is, everything that isn't a plant) must eat. Food web.
When wood is exposed to water and fungi, deterioration sets in (microscopic organisms). Fungi can only colonise wet, constantly moist wood; dry wood is inhospitable to mycelium. However, there are over as 5 million different kinds of fungi in the soil and atmosphere around us. Many, like yeast and fungus, are useful, but there are also harmful varieties. Many different organisms can cause wood decay, however they can largely be grouped into three categories based on the ways in which they interact with the wood itself.
- Brown Rot: Also known as "dry rot" due to the fact that the wood's surface seems dry, brown-rot fungus attack the wood's cellulose. Cubical fracture occurs as the wood contracts, turns dark, and cracks into tiny pieces as the cellulose is consumed. Brown rot grows rapidly at temperatures between 65 and 90 degrees F, and it can cause extensive damage.
- White rot is indicated when wood turns a yellowish , light yellow colour and becomes spongy to the touch. White-rot fungi, in contrast to their brown-rot counterparts, only attack the darker lignin in wood, leaving the lighter cellulose intact. White rot, like brown rot, develops when the temperature is in the 65°F to 90°F range.
- Decomposition by soft-rot fungus is more slower than by brown-rot fungi or white-rot fungi, but it can occur at temperatures between 0 or 110 degrees Fahrenheit, when the former two species would perish. If the conditions are correct, soft-rot fungus can infest a home and cause the wood to deteriorate into a honeycomb pattern. These fungi are more typically seen in dead trees and logs.
Where Specifically Could My House Be In Danger?
Because wood rot typically originates in damp places that don't get dry enough just to dry out, it often goes undetected until a renovation activity reveals it. This article will discuss the most likely entry points for wood rot and how it might spread across a building.
Windows
Modern windows are made to be watertight, but even a little crack that isn't caulked properly might let rain in, rotting the wood with in wall below. Wetness persists in the wood because it is not allowed to dry out by exposure to air or sunlight. This makes it possible for fungus to flourish. Older wooden windows have a tendency for water to pool just on horizontal sills, which can lead to the paint cracking and water seeping in. The windows are considerably more in danger now.
Accessible External Doorways
Similarly to windows, any space between a door and its siding (or threshold) is an open invitation for water to seep in and promote the growth of wood rot. Many times, when owners decide to instal a new door, they find rot in the old one. Removal of the old metal door reveals rotted timber in the supporting structure.
Constructing An Outdoor Deck
Stair treads and other horizontal decks can potentially become pools of water. Water-resistant but not watertight and susceptible to rot, treated decking timbers are widely available. Untreated pine is used to construct these balusters, which are then painted to withstand the elements. Fungi can thrive because moisture is prevented from evaporating from under the baluster.
Basements
High levels of humidity and moisture are common in basements because their concrete walls are surrounded by wet soil. Humidity levels in damp basements can rise to the point that water vapour condenses on the walls and ceiling joists, causing structural damage. Once wood rot establishes itself in this location, it can spread unnoticed until it has done significant damage to the building.
Shower Rooms
Every area in the house where there is a plumbed-in water fixture is at risk. This includes the kitchen, bath, washer and dryer, and room (with a water heater). Leaks surrounding the water supply cables and drain pipes keep the region wet, which is conducive to the development of wood-rotting fungi.
Roofing That Has Sustained Damage
If shingles be missing or damaged, water can seep in and rot the roof deck and attic framing lumber. Because of this, the wood may deteriorate over time. Damaged or missing shingles.
The Function Of Bacteria Exactly What Mechanism Do They Employ To Rot Wood?
Bacteria are single-celled microbes, although they belong to a different kingdom of life than fungi. Several of them are more similar to fish than to land plants, while others have more in common with animals that require oxygen for survival. There are thousands of different kinds of bacteria, and many of them will sporulate if the conditions are right.
With What Do Bacteria Have To Maintain -Alive
Although bacteria often prefer a more humid wood environment than do fungi, both can thrive within a certain humidity range. Many bacteria can able to live in the air unless they land on a damp surface, at which point they die. Certain bacteria can only live in water at all times. The vast majority of microbes can swim and crawl. Some of them wriggle when they're hungry or lonely, while others have lot of tiny legs that they utilize to crawl or swim with.
Check out our range of timber repairs Melbourne at Hitch Property Constructions.
The Question Of Our Wood What Are These Organisms Consuming?
Depending on the relative humidity in the air, wood's natural humidity—perhaps 5 to 15% (after resting in your garage over six months)—may increase or decrease. Humidity throughout the summer fluctuates between 10 and 95%.
Measurement of water vapour in the air is accomplished via the humidity scale. This air is 10% humid, or full, if you will. That air's capacity has been dissolved by 90%, hence the humidity is 90%. Precisely one hundred percent humidity and rain.
The percentage of relative humidity for wood (for example, ten per cent). The percentage of moisture in the wood. Humidity isn't the proportion of water by mass that exists in the air, but rather the amount of water that can be contained by the air. The percentage of water in the air is proportional to the temperature, but averages out at roughly 1% by weight.
Water can be held by wood firmly for a short period of time, and then only sporadically and with diminishing strength. Wood dries out by evaporation when the relative humidity of the air is low. Water vaporises from damp wood whereas it is absorbed by dry wood at high humidity. When moisture leaves and enters wood, it "breathes."
The Wood's Physical Qualities Change Depending On The Moisture Content.
As a result of the high water content in plant wood, the more flexible smaller branches could be bent in a wide variety of orientations. Dried wood is more stiff than freshly cut wood. You might find a dry, brittle piece of wood in the desert, or a dead twig on a tree.
Wood becomes malleable and almost "rubbery" when exposed towards the hot steam that results from boiling water, allowing it to be moulded after being placed in a box. While returning to its original humidity and ambient temperature, the substance maintains its altered shape as it gradually cools. Steam-bending is a technique used to construct the bent ribs of many various types of small boats.
Because Wood Is Porous, It Can Hold Water And The Organisms That Cause Rot.
If you submerge a piece of wood, it will float halfway up and halfway down. Wood has a lower density than water. Half of a piece of wood is air before it rots. When wood is damaged by water, it becomes "waterlogged," meaning that water has saturated the majority of the wood's volume and caused it to either sink because of a lack of air pockets or float because of a reduction in density. You may have noticed the difference in weight between dry and soggy wood.
Preventing Wood From Rotting Due To Water Intrusion
That moisture that causes decay can often be traced directly back to a problem with draining or a leak. There will be moments when identifying the perpetrator will be more difficult. Damage from rot might be hard to assess without first determining the source of the water. It can make it tough to budget for fixes in advance.
Remove Wood-Rotting Fungi And Prevent Further Damage.
Borate (also known as boric acid) is a fungicide that has been shown to be effective against wood rot. This can be applied to wood during construction for either treatment of an active rot fungus or prevention of future rot.
Whether Or Not Wet Wood Rot Can Be Fixed Or Treated.
Wet rot usually results in less harm than dry rot does. In most cases, the rot will cease spreading once the water source is cut off. The use of a fungicide, such as borax, after water has been removed can help prevent future cases of moisture rot.
If the damaged region is small, accessible, and does contribute to the structural integrity of the wood, you can likely remove any damaged wood and reconstruct it using wood filler. If you rebuild and seal the region, you can fix the wet wood rot. If damp wood rot has spread across a considerable region or has affected a load-bearing piece of the wood, it must be replaced.
Is There Any Way To Treat Or Fix Dry Rot In Wood?
Dry rot is much more difficult to fix than wet rot. Because dry rot can spread rapidly via permeable masonry and through the wood itself, it is of the utmost significance to eradicate all phases of the fungus immediately soon as possible. The most effective way to accomplish this is to first remove but then replace the diseased wood, and then treat the remaining timber with a fungicide.
Does Rotted Wood Need To Be Replaced?
Due to the prevalence of wood rot, softwood needs to be replaced has soon as feasible. It's recommended to cure wood if it's discoloured but not soft. Prevent any damage to the wood by fixing any leaks and drying it out with a dehumidifier. Use a preservative such Woodlife Copper Coat, which is based on copper or borate, after the wood has dried. Keep an eye out for any decay in the wood.
When I Ask, "How Can I Avoid Such Issues In The Future?"
Preventing wood rot is of utmost importance. Preventing rot from occuring is easier and more cost-effective than fixing it. In order to prevent fungi from colonising the wood within your home, you should take the following precautions.
- Use caulk to fill in any gaps around the frames of your windows and doors.
- To repair a leak, remove the old, hardened caulk and refill it with new.
- Keep your gutters clear at least two times a year to avoid the damage that can be caused by water spilling over the gutter's edge and leaking down your home's side.
- Make sure the doors are protected from the elements by installing an overhang.
- Invest in a high-quality dehumidifier for the basements or other damp area of your home.
- Putting up ventilation system in bathrooms is a great way to get rid of the stale air that builds up after a hot shower.
- Fix any flaking or cracking paint on the outside windows and siding.
- Clear any puddles from a deck or patio as soon even as rain stops falling.
We have a wide range of Melbourne timber repairs for your home renovations. Check out Hitch Property Constructions.
Just How Rotten Does Something Have To Be Before It's Considered Ruined?
If the object is mushy toward the touch (a symptom of wet rot) as well as the wet wood muck may be removed with such a sweeping motion of the hand, it is extremely improbable that the piece can be recovered.
If more than 20% of your wood is rotten, you'll have to make a tough choice.
You can either cut out the rotten piece and utilise what's left of the board, which will be shorter than it was before, or you can just replace it.
It's more challenging to spot the damage and it's probably worse than first thought because the rot travels all through timber rather than appearing in a particular corner or section.
You may either repair your lumber or prevent more moist and dry rot by employing one of the previously mentioned strategies.
When you're done, it's important to take the procedures necessary to cure and seal the wood so that this doesn't happen again.
Preventing wood rot is difficult, but these measures will make it easier.
Conclusion
Any exposed wood, whether indoors or out, will eventually rot if exposed to enough moisture or time. Rotted wood can be found almost anywhere, but the most common places are in pipes, basements, door jams, decks, and fences. An effective repair requires treatment of both the rotted and unrotted wood. When filling wood, epoxy or polyurethane is the most effective agent. Make fake grain lines with a utility knife before staining.
It's not safe to assume it's sound just because it appears to be so, as rot often occurs under paint. Epoxy liquid, applied evenly and deeply into the surface, can fix severely damaged wood. Use a router with a V-shaped bit to quickly remove rotten wood. After the first application of Wood Restorer, damaged wood can be treated with it for another four to six applications. It's also necessary to remove any grit, rust, or primer from the wood's surface before moving forwards.
The Patch should be glued to the wood with polyurethane glue. As it cures, polyurethane glue expands to fill even the tiniest of gaps. Wait about 6 hours for the urethane glue to dry and set completely. Wood filler can be used without worrying about it sticking to or breaking glass or plastic. In some cases, wood filler may change the colour of the affected area slightly.
If you want a flawless, streak-free primer application, spraying it on is your best bet. Wet or dry, wood decay can occur in any structure, necessitating its removal if repair is not an option. Roofing shingles that are missing or broken, improper drainage, poorly fitting doors and windows, improper stone pointing, and excessive moisture are all potential causes of rot. Get rid of rotten wood with the help of a 5-in-1 craftsman's tool or a putty knife.
Content Summary
- Support timbers and beams, floor , ceiling joists, and roof decking can all be damaged by wood rot.
- The expense to replace rotten wood might easily run into the tens of thousands.
- The most popular building material is wood, so understanding what caused lumber rot, how to stop it, and what you should do if you find it are all essential.
- Despite being exposed to the elements, wood can be preserved.
- Water is far more destructive to wood than either mould or rot.
- How can we restore wood that has been ruined by water?Guidelines for rescuing rotten timber and a check list to establish whether or not the wood is deteriorating are provided.
- Termites love the wetness that comes with wood rot.
- Have you ever pondered the cycle of wood's growth, decline, and eventual demise?
- Feasts on wood and lives a humble existence.
- Mushrooms are rooted organisms that get their nutrients and energy from their food rather than the sun.
- Many different organisms can cause wood decay, however they can largely be grouped into three categories based on the ways in which they interact with the wood itself.
- Because wood rot typically originates in damp places that don't get dry enough just to dry out, it often goes undetected until a renovation activity reveals it.
- This article will discuss the most likely entry points for wood rot and how it might spread across a building.
- The windows are considerably more in danger now.
- Similarly to windows, any space between a door and its siding (or threshold) is an open invitation for water to seep in and promote the growth of wood rot.
- The percentage of relative humidity for wood (for example, ten per cent).
- The percentage of moisture in the wood.
- Wood dries out by evaporation when the relative humidity of the air is low.
- As a result of the high water content in plant wood, the more flexible smaller branches could be bent in a wide variety of orientations.
- Wood has a lower density than water.
- Half of a piece of wood is air before it rots.
- Damage from rot might be hard to assess without first determining the source of the water.
- Borate (also known as boric acid) is a fungicide that has been shown to be effective against wood rot.
- Wet rot usually results in less harm than dry rot does.
- If you rebuild and seal the region, you can fix the wet wood rot.
- Dry rot is much more difficult to fix than wet rot.
- Prevent any damage to the wood by fixing any leaks and drying it out with a dehumidifier.
- Keep an eye out for any decay in the wood.
- In order to prevent fungi from colonising the wood within your home, you should take the following precautions.
- Use caulk to fill in any gaps around the frames of your windows and doors.
- To repair a leak, remove the old, hardened caulk and refill it with new.
- Make sure the doors are protected from the elements by installing an overhang.
- Invest in a high-quality dehumidifier for the basements or other damp area of your home.
- Fix any flaking or cracking paint on the outside windows and siding.
- If more than 20% of your wood is rotten, you'll have to make a tough choice.
- You may either repair your lumber or prevent more moist and dry rot by employing one of the previously mentioned strategies.
- Preventing wood rot is difficult, but these measures will make it easier.
FAQs About Wood Rot
Look for signs of wood damage around the home. This comes in many forms: discoloration, shrunken size, cracks, and splintering. As rotting progresses, it breaks down the cellulose in the wood. This causes the wood to become soft and dark in color; it also gets smaller in size as the cellulose is consumed.
When you come across rotted wood in your old house projects, instead of replacing the damaged wood, you also can repair it with specialty epoxy penetrants (also called consolidants) and fillers to make repairs. Not only is this faster, but the fixed wood is stronger than the original.
Signs of dry rot include:
- damaged or decaying timber.
- damp or musty smell.
- deep cracks in the timber grain.
- brittle timber or timber that crumbles in your hand.
- concentrated patches of orange–brown spore dust.
- grey strands on timber.
- fruiting bodies that look like large mushrooms.
Borate treatment prevents wood rot in new wood and will kill fungus and rot-causing organisms. Treatments made of ethylene glycol kills both wood-consuming fungi and insects that are drawn to damaged and weakened wood. Both borate and glycol treatments soak into dry wood because they are water-soluble.
However, in most cases you can stop wet rot by treating the timber with a fungicide. The treatment of wet rot involves applying a fungicide during the drying out period. The fungicide can be supplied in concentrate form (usually for professionals for use over large areas) or as a ready to use product.