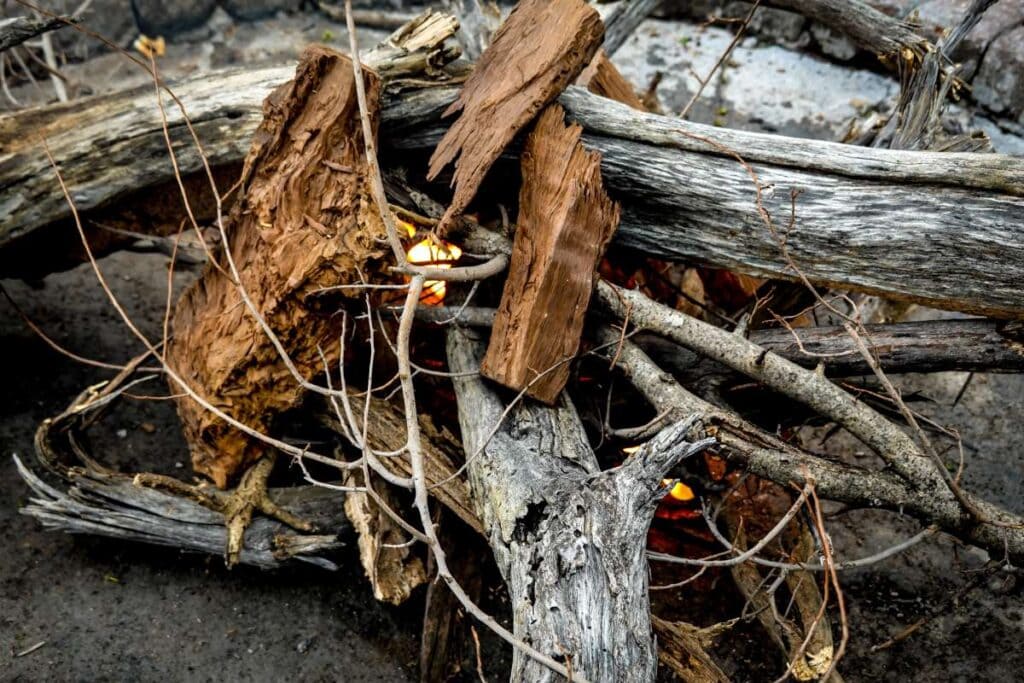
The words "timber degradation" are the last thing a homeowner of an older property wants to hear. When homeowners discover unwelcome problems like rot or wood insects consuming their woodwork, they often panic and resort to extreme measures that can save their home.
Insecticides, preservatives, and other chemical treatments are not always the best option. Paying a skilled timber study to identify the issues with your building and recommend a more cost-effective solution is preferable to making an impulsive financial investment in a quick remedy. These options are usually more cost-effective and time-efficient in the long run.
You definitely do not want to hear about timber degradation from your surveyor. It may require expensive maintenance or medical care. If you want to save money on repairs, avoid emergency phone calls concerning wood deterioration caused by dry rot or termites, you should find another method.
By managing humidity, building owners can forestall the spread of mould and the invasion of unwanted insects.
At Hitch Property Constructions, we offer timber repairs work from simple timber repair to almost new structures, renovations, and extensions.
What Exactly Is Dry Rot?
Fungi can cause dry rot, commonly known as brown rot, which can ruin any wooden parts of your home. Dry rot is caused by fungi and results in the breakdown of the cellulose and hemicellulose that give wood its strength and durability. In addition to weakening the wood and giving it a brittle texture, this treatment can also make it look more blocky.
Dry rot can only infect wood if the wood is damp, meaning it has a moisture level of greater than 20%. It doesn't take long for dry rot to spread. Therefore, any plan for getting rid of dry rot should revolve around cutting off the moisture supply that it needs to thrive. Keep on reading for more tips on how to prevent dry rot.
What Are The Means By Which Dry Rot Can Quickly Spread?
It is possible to propagate the dry rot fungi by breathing in its spores. If the seeds fall onto wood that has been soaked for an extended period of time, they will germinate.
- The wood wasn't kiln-dried to remove excess moisture (to a level below 20%) before it was utilised in the building.
- The wood is stored in a particularly damp part of the house.
- There has been immersion in a big body of water, such as during flooding caused by a broken pipe.
The spores require not just moisture but also a food source (wood), oxygen, and ideally warm temperatures in order to germinate and thrive.
In the absence of treatment, dry rot can weaken wood to a point where it collapses.
Learn The Signs Of Dry Rot So You Can Fix It
- Check out the timber! At first glance, the fungus resembles cotton wool and, in humid conditions, may even have water droplets floating on its surface.
- Verify that there is no hollowing out or shrinking.
- The wood is browning and cracking, so be aware of this.
- Keep an eye out for wood that has a flat, skin-like growth, perhaps with silvery-grey tones like the exterior of a mushroom. It peels quickly and typically has a light purple and yellow pattern.
Factors Contributing To Wood Rot
Increasing moisture or dampness is the most common cause of timber degradation, however old age is also a factor. Because dampness promotes the growth of mould and fungi that eat away at wood, it is inextricably related to the spread of decay-causing fungal illnesses like dry rot or wet rot.
Sub-floor vents are typically installed to offer this necessary dry, well-ventilated environment for sub-floor timbers (airbricks). Dampness and wood rot are both diminished when vents are not blocked or concealed.
Oversaturation of wood fibres by water from leaky roofs or moist walls can lead to degradation, which in turn invites wood-boring insects. Wood that has been structurally compromised by bowing or bending can also serve as a magnet for wood-boring insects, so take care.
Rot: Dry Or Wet? Poll On The Risk Of Dry Rot
When spores in the air land on wet wood and germinate, the result is dry rot. It ranks up there as one of the most serious issues related to real estate. As it rapidly spreads, it weakens the integrity of the wood.
Dry rot, despite its name, requires moisture in order to flourish. It's not easy to notice since it likes dark, out-of-the-way spots such under floors, behind wainscoting, in attic, or from behind plaster that blocks out the light. Large cuboidal cracks all across grain and a white development of fungal filaments (mycelium) on the backside of affected wood characterise it. Spore dust with an orange or red hue may be present when a fungus grows a fruiting body (mushroom). The infectivity of dry rot can travel many metres from its origin.
However, while wet rot is not quite as destructive as dry rot, it can still lead to problems. If untreated, it will attack damp wood and cause structural damage. Fungal spores can hatch and release enzymes break down cellulose when wood absorbs too much moisture, causing wood wood to deteriorate. A musty odour, cracking of the grain, softening of the wood, and discoloration are all signs of wet rot. Wet rot develops only in damp environments.
Attacking Both Dry And Wet Rot
The first step is to determine what's allowing the moisture to get in, and then fix it. Examination of Dry and Wet Rot
Rust In Dry Places
Since dry rot can travel along with other building components like iron, "exposed work" is necessary to assess the full scope of the epidemic. In order to treat the mycelium, the fungal growth on the walls and beams, the afflicted wall plaster must be removed.
After holes are made in the wall all around afflicted masonry's perimeter, a masonry antimicrobial is pumped into the holes. Then, a top is applied to all of the masonry's visible surfaces. The masonry is essentially "sterilised" by the treatment, rendering any future mycelium formation of dry rot impossible and hence rendering any more damage impossible to occur.
Damp Rot
Deteriorated wood must be removed to "sound" wood, which really is wood that is still in good shape and structurally sound, and any rotten wood must be replaced. A fungicidal spraying that is HSE-approved, seems to have a low scent, is non-flammable, or dries quickly must be used to treat the timbers.
Dry Rot Treatment
Restorations with epoxy. Any holes or crevices in the harmed wood should be filled with epoxy. In addition to stopping the spread of the rot, this will also strengthen the wood's underlying framework.
An antifreeze available for purchase. Dry rot can be treated with antifreeze, that will kill the fungi and prevent further infection.
Metallic copper compounds Dry rot necessitates removal of the damaged part of wood before new wood can be successfully spliced in. Then, before putting in the replacement wood, coat the existing wood thoroughly with a copper compound.
Check out our range of timber repairs Melbourne at Hitch Property Constructions.
Avoiding Wet Rot
Dry rot is easily avoided by taking a few precautions. Take these precautions to protect the wood inside your home from excessive humidity:
- Siding: Hire a professional who knows how to properly seal and instal wood siding.
- Prime all six sides of the wood before painting it, especially if it will be exposed to the elements.
- Water damage, mould, and dry rot can all be prevented with an annual roof inspection. Ease the burden of rainwater on your home's windows or foundations by setting up a gutter system.
- Leaks in the plumbing system are a leading source of dry rot. Look for leaks in the plumbing behind sinks and behind commodes. When you discover any, get them fixed immediately.
- Ventilation: Install fans in your kitchen, bathrooms, and attic to reduce condensation.
- Be sure to seal your deck correctly. If you're having a carpenter construct a new deck for you, they should build it at a modest incline so that rain may run off of it.
- When working on your yard, make sure that sprinklers are not aimed in a direction that would cause them to spray water onto the siding of your house.
The Prevention And Treatment Of Dry Rot
Only wood that has been exposed to high levels of moisture, more than 20%, will dry rot. To get rid of dry rot, you need to take away its water supply.
If you want to know why wood gets damp, you can't just ask it. Washers, shower pans, bathtubs, dampness, etc. are common culprits. Going to leak roofing, increasing dampness, or damp walls are all external causes of moisture. As long as the wood is given time to dry in and the moisture problem is addressed, dryness rot can be managed.
In some cases, it is neither feasible nor practicable to dry wood over a long period of time. Take supplementary precautions to avoid reinfection. Substitute pre-treated wood for any impacted timber. In order to prevent rot, a fungicide should be applied to any dry wood that is susceptible to it. Physical confinement and masonry sterilisation are both recommended for isolating dry rot.
Waterproofing paint and humid membranes are recommended for outside wood to keep water out. Be mindful of the potential for water damage at seams and similar locations. Gutters should be cleaned of leaves and debris, and connectors and rubber seals should be inspected to prevent water damage to exterior walls.
Remove warm, damp air from wooden floors by replacing damaged or inefficient extractor fans in the bathroom and kitchen (like window frames). Dehumidifiers might not be necessary in issue properties if humidistat fans were updated.
Condensation can easily avoided with the installation of contemporary sub-floor vents in a home (air bricks). To contain the spread of steamy air, shut the door behind you as you shower or take a bath.
Having a plan in place for the movement of moisture around your property is essential if you want to prevent timber deterioration, which occurs at humidity levels of 20% and higher.
Preventing timber degradation in your home is possible with the right preventative measures.
How Severe Is Dry Rot?
Early detection is key to effectively treating localised dry rot. Its contagious nature can rapidly worsen an outbreak, and estimating the cost of repairs requires first examining the extent of the destruction. Pretreatment stripping of the property is possible.
If you fix the wet spot, the fungus won't have a chance to germinate, and it will die from lack of moisture. Dry-rotted rooms should have ventilation improved (a dehumidifier could assist) and the moisture source fixed. There may be a need to remove badly damaged timbers and treat the remaining woodwork if the rot has spread.
Substituting Wood
Worn down or decayed timber has to be replaced. Bearer timber parts are the most at risk since they absorb moisture directly from the wall structure.
Therefore, it is just necessary to replace the wood's ends. Traditionally, builders would use steel plates and bolts and wooden connectors to join together new parts. However, the steel plates might be an eyesore if the beams are exposed. Investigate the air flow underneath wooden floors. When airbricks are blocked, condensation forms on the timbers, causing them to deteriorate at the ends and the middle of the span.
Large, broken beams can be fixed with epoxy resins. This technology is both aesthetically pleasing and cost-effective since it allows for repairs to be conducted with minimal disruption to the surrounding construction and without the use of unsightly steel plates.
We have a wide range of Melbourne timber repairs for your home renovations. Check out Hitch Property Constructions.
How Should Dry Rot Be Treated And Repaired?
Dry-rotted wood can be fixed in a number of different methods.
Before addressing dry rot damage, make sure there isn't a moisture problem in the house.
Additions of moisture will dilute the effectiveness of your treatment. Because they dissolve in water, these compounds can seep into porous materials like masonry and wood that have been exposed to moisture.
If you suspect Dry Rot in your house, you may find out how far it has gone by using Fugenex sensor sticks.
Even if the rot is isolated to exposed joists, the joists and any masonry they contact must be treated.
Replace wood that has been severely damaged by rot. If you're looking for further details on how to put wood to use, visit the Timber Trade Association website.
After this is complete, the surrounding brick and wood must be treated for the possibility of fungal infiltration, which may be too small to be seen with the human eye.
The plaster will need to be stripped and the wall treated if dry rot is present; only then can new plaster be applied.
Most structures rely on timber in some capacity, and as such, it's important to treat it with respect to keep it in good condition and preserve its worth. This degree of rotted wood or rotted wood infestation can be ascertained through a professional inspection.
Proper maintenance can prevent timber rot from destroying your home and your cash account. Be cautious of potential issues and make sure your home has adequate ventilation throughout the winter.
Conclusion
Fungi cause dry rot, which weakens wood by eating away at its structural components, cellulose and hemicellulose. Wood with a moisture content of more than 20% is susceptible to infection by dry rot fungi. Dry rot can quickly spread throughout a building. It is important to recognise the symptoms of dry rot in order to make the necessary repairs. Wood with a smooth, thin growth pattern, resembling the skin of a mushroom; it may have a silvery grey coloration.
Dry rot thrives in damp, secluded areas, like beneath floors or behind wainscoting. When wood absorbs an excessive amount of moisture, it can trigger the hatching and release of enzymes that break down cellulose, leading to the deterioration of the wood. Using antifreeze as a treatment for dry rot is an effective way to eliminate the fungi responsible for the problem and stop any further infection. Only in wet conditions can rot develop. An annual roof inspection is essential for avoiding problems like water leaks, mould growth, and dry rot.
Common causes include washing machines, shower stalls, bathtubs, humidity, and more. As long as the wood is allowed to dry out, dry rot can be controlled. Wood can last longer in your home without deteriorating if you take care of it properly. We recommend boosting ventilation in dry-rotted rooms (a dehumidifier could assist) In the event that the rot has spread, it may be necessary to remove severely damaged timbers and treat the remaining woodwork. Using Fugenex sensor sticks, you can determine the severity of dry rot in your home.
The joists and any masonry they touch must be treated even if the rot is contained to just those areas. If you add water to your treatment, it won't be as effective.
Content Summary
- Paying a skilled timber study to identify the issues with your building and recommend a more cost-effective solution is preferable to making an impulsive financial investment in a quick remedy.
- Fungi can cause dry rot, commonly known as brown rot, which can ruin any wooden parts of your home.
- It doesn't take long for dry rot to spread.
- Therefore, any plan for getting rid of dry rot should revolve around cutting off the moisture supply that it needs to thrive.
- Keep on reading for more tips on how to prevent dry rot.
- In the absence of treatment, dry rot can weaken wood to a point where it collapses.
- Because dampness promotes the growth of mould and fungi that eat away at wood, it is inextricably related to the spread of decay-causing fungal illnesses like dry rot or wet rot.
- When spores in the air land on wet wood and germinate, the result is dry rot.
- As it rapidly spreads, it weakens the integrity of the wood.
- However, while wet rot is not quite as destructive as dry rot, it can still lead to problems.
- A musty odour, cracking of the grain, softening of the wood, and discoloration are all signs of wet rot.
- Dry rot can be treated with antifreeze, that will kill the fungi and prevent further infection.
- Leaks in the plumbing system are a leading source of dry rot.
- Be sure to seal your deck correctly.
- To get rid of dry rot, you need to take away its water supply.
- Remove warm, damp air from wooden floors by replacing damaged or inefficient extractor fans in the bathroom and kitchen (like window frames).
- Condensation can easily avoided with the installation of contemporary sub-floor vents in a home (air bricks).
- Preventing timber degradation in your home is possible with the right preventative measures.
- Early detection is key to effectively treating localised dry rot.
- Pretreatment stripping of the property is possible.
- There may be a need to remove badly damaged timbers and treat the remaining woodwork if the rot has spread.
- Investigate the air flow underneath wooden floors.
- Additions of moisture will dilute the effectiveness of your treatment.
- If you suspect Dry Rot in your house, you may find out how far it has gone by using Fugenex sensor sticks.
- Replace wood that has been severely damaged by rot.
- The plaster will need to be stripped and the wall treated if dry rot is present; only then can new plaster be applied.
- Proper maintenance can prevent timber rot from destroying your home and your cash account.
FAQs About Wood Rot
Lab experiments have recorded that dry rot spores can germinate approximately seven to ten days after the wood has become damp enough. Older spores can take longer to germinate. As mentioned earlier, though, it can take a long while for signs of dry rot to appear after germination.
Bleach can be used to effectively kill wood rot and stop its spread. It attacks the fungi that causes rot and stops it from growing. Bleach can be applied as a spray or directly on the rotten areas with a cotton swab.
Wood rot can cause a variety of issues, including serious structural damage and costly repairs. The most common types of wood decay fungi are brown rot, white rot, and soft rot. Learn more about the three different types of wood rot and how to spot them
If a piece of wood is rotted, don't burn it in your fireplace. Rotten wood is less dense than solid, unrotten wood. And with a lower density, it won't produce as much heat when burned. Furthermore, rotting typically occurs from exposure to water or moisture.
Wood rot looks like decay, whereas mold on wood usually looks like a discoloration. While mold is by no means good, it is better than wood rot for homes. However, as both wood rot and mold form in damp and humid environments, the presence of mold can signal that wood rot is soon to follow.