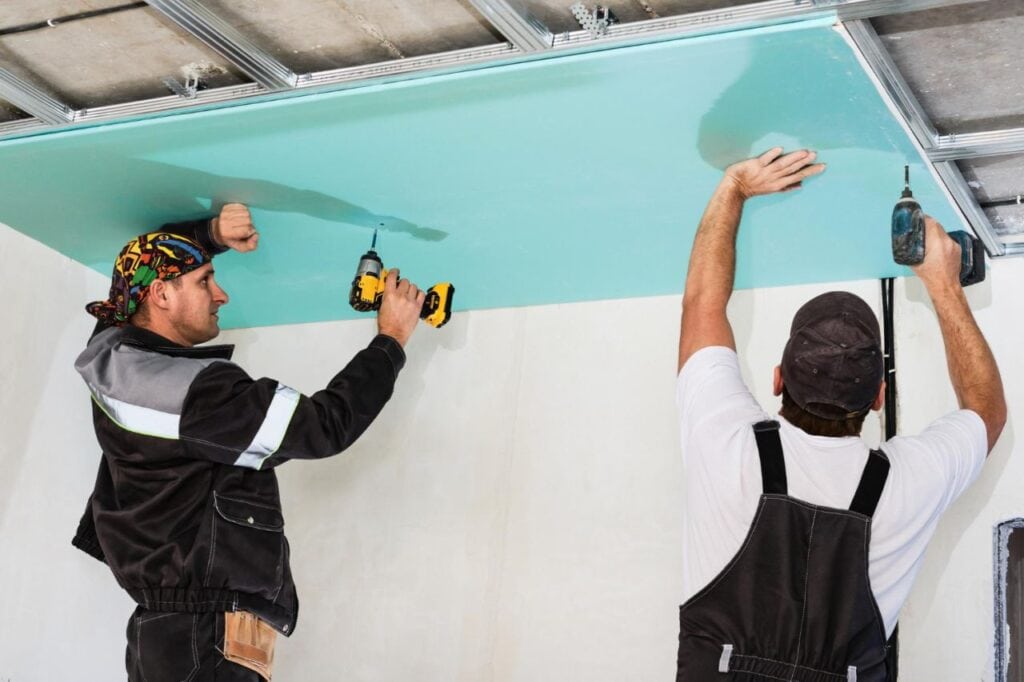
Plastering is an essential part of constructing or renovating any structure. Plastering entails covering ceilings, walls, and other surfaces to achieve a thin layer of plaster and a uniform appearance. Plastering may appear to be unimportant but take into account its significance.
Not only does it make a structure look better, but it also serves practical purposes like protecting it from the elements and reducing noise.
This article will examine the many facets of plastering, including its methods, varieties, and quality-influencing factors. We will also examine plastering's role in building quality and durability.
The Importance Of Plastering
Plastering entails applying a thin coat of plaster to walls, ceilings, and other surfaces to achieve a uniform and smooth appearance. It's been done for a long time, even by ancient peoples like the Greeks, Egyptians, and Romans. Plastering is a common method of interior and exterior finishing in modern construction.
What Are The Benefits Of Plastering?
If you plan on doing interior remodelling soon and need your walls plastered, now is the time to do it. Read on to learn more about the practical applications and benefits of plastering. Why should one plaster a wall? But first, let's define this thing called "plastering."
Quick Refurbishment
Plastering is a great alternative to drywall repair when you need to update your walls quickly. Concrete membranes can replace more expensive materials like marble, tiles, and other stones to significantly reduce construction costs.
Laminate plasters are another option for flooring, offering durability and longevity.
Strengthening Walls
Plaster murals are much more robust than those on dry walls.
These walls don't require any upkeep and can last for decades. Plastering is recommended if you want to reduce the frequency of wall repairs and the associated costs.
Styling And Aesthetics
Having nothing but blank, smooth, untempered walls in your lovely home's living space is a waste. The fullness that plaster provides highlights the home's natural beauty.
Plaster moulds applied to walls and ceilings can often achieve the desired "Wow!" effect while being relatively inexpensive.
The choice of plaster moulds requires careful consideration of many factors, including the project's overall theme, colours, size, and design. A slight shift in colour or depth would transform it into a masterpiece.
Durability
Plaster improves the strength and longevity of walls, adding to their aesthetic appeal. Plaster is more robust and long-lasting than drywall if properly mixed and applied.
Evaporation of water from the plaster mixture triggers a chemical reaction that fortifies the walls. In most situations, the durability of plaster makes it preferable to use.
Plaster's durability is also affected by the lath—or backing—used to secure it. Traditional wooden lath strips deteriorate over time, but new metal lath or solid backing boards will last a lot longer.
Noise Absorption And Fire Retardant
Comparing a room with modern drywall to one with traditional plaster and lath reveals a noticeable increase in ambient noise. Lime plaster is denser than the latest gypsum board, and the irregular shapes of the keys between the walls serve as acoustical and sound-absorbing elements.
Carbonated lime (lime that has been cured for months) has been shown to slow the spread of fire compared to standard drywall, adding to the traditional lime plaster material's reputation for fire resistance.
However, fire may also have less oxygen to work with if there is less room or air between the layers of a wall or ceiling.
Easy Installation
Plaster's ease of installation is a major plus. In addition, the lack of dust during installation is a major plus, with the exception of the minute amount of dust created when the powder is first mixed with water.
Plaster also requires no sanding and can be applied to a wall in less time. You can apply multiple coats without waiting for each one to dry, and there's no need to sand between them. Plastering a wall is quicker and cleaner than using other materials.
What Kinds Of Plastering Materials Are There?
Plastering has been used for centuries to protect and conceal building surfaces like walls and ceilings. The process involves applying a compound to a surface in order to achieve a uniform sheen.
Different types of plastering materials offer different advantages. These materials can vary in composition, texture, and function to meet any project's requirements.
Cement Plaster
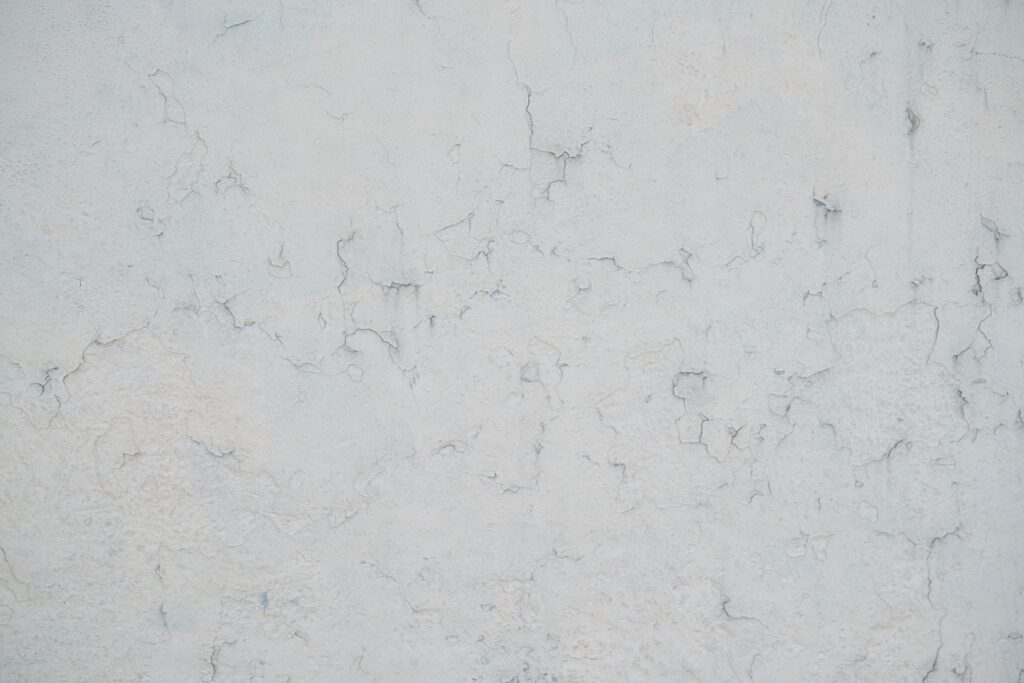

Plaster made from cement is widely used in building and remodelling projects. Smooth and even walls and ceilings can be achieved by applying a mixture of cement, sand, and water. The coating is applied with trowels, floats, brushes, and other tools to ensure consistency and precision.
Cement plaster is often applied in two stages: scratch and finishing coats for increased protection and durability.
Concrete has two layers: the scratch coat, which is made of cement and coarse aggregates like sand or gravel, and the finish coat, which is made of finer materials like lime or gypsum, to create a smoother finish.
When placed correctly and allowed to dry, cement plaster can result in an attractive, long-lasting surface that can be painted over if necessary.
Mud And Clay Plasters
Plasters made from clay and mud have been used for centuries in building and remodelling. Natural clay and mud are combined with other ingredients like straw and debris to create a thick paste-like material used in their production.
Durable finishes for interior and exterior walls can be achieved with clay and mud plasters.
They work particularly well for making decorative patterns and designs in the form of swirls and geometric shapes on the walls and ceilings.
When it comes to home energy efficiency, clay and mud plasters are a more economical option than traditional lime plasters because of their superior insulation properties.
You can apply them with a trowel or a wooden float in multiple coats to achieve different effects, such as a smooth finish or a rough surface. Plasters made of clay and mud can persist for decades without major repairs or replacements if they are cared for properly.
Gypsum Plaster
Gypsum plaster is a common building material that creates a flat, uniform surface on walls and ceilings. Calcium sulphate hemihydrate is mixed with water and sand to create this material to form a paste.
Gypsum plaster provides a smooth, long-lasting surface that can be painted or left unfinished.
In most cases, it is troweled on in several layers, with each layer being given time to dry in between. Gypsum plaster has better-insulating properties than lime plaster and doesn't need to be cured before use.
Gypsum plaster has a long lifespan and requires nothing in the way of repairs or replacements if cared for properly. As an added bonus, it has many practical uses, including fabricating decorative effects and restoring damaged surfaces.
Lime Plaster
Lime plaster has been widely used in construction for many decades. It is applied to walls and ceilings to make a more permanent finish and is made of lime, sand, and water.
Lime plaster creates a flat surface that can be painted or left unfinished to suit personal taste. A straight steel edge, a wooden float, and other tools are used during the application process to ensure uniformity.
Sand-faced and rough-cast finish are two examples of the many methods to achieve the desired surface texture. Lime plaster is a great choice because it protects against moisture and other elements while also looking great.
Plastered surfaces can persist for decades with occasional maintenance and repair if treated with the respect they deserve.
Plastering Techniques
The art of plastering entails applying a thin coat of plaster to a surface in order to achieve a uniform and smooth appearance. Skimming, floating, and rendering are just a few examples of plastering techniques used to achieve different aesthetic results.
Skimming
Skimming is a plastering method for creating a smooth, even finish by applying a thin coat of plaster to a surface. Walls and ceilings inside a building that are in good condition and don't need extensive repairs are perfect candidates for skim coating.
Plaster is skimmed over an existing surface to create a uniform and smooth finish. Then, multiple, increasingly thin coats of plaster are applied until the desired sheen is achieved. The final coating is flawless because it has been polished and smoothed.
Skimming has the benefit of being a fast and cheap way to update the look of a room. It can hide flaws and produce a uniform surface ready for further embellishment with paint or wallpaper.
Skimming, or plastering, is a job best left to professionals. The plasterer's skill lies in their ability to apply the substance uniformly and smoothly. Getting the finish right the first time is vital since any faults in the plaster can be difficult to hide once the plaster has cured.
Floating
To "float" a surface, a thick coat of plaster is applied, and then the surface is smoothed out with a float or trowel. Exterior or interior walls with uneven surfaces that need smoothing are perfect candidates for floating.
Plaster is applied with a trowel or hawk and allowed to dry thoroughly before floating. The plaster is then finished with a flat tool called a float, typically wood or plastic. The plaster dries quickly, so the plasterer needs to work quickly to apply it evenly and smoothly.
Floating can smooth out an otherwise uneven surface and produce a uniform coating. A textured finish or stippled look are only two examples of decorative effects that floating can produce.
To get a professional-looking float job, you need a plasterer with experience. The plasterer's speed and precision are essential for producing a high-quality finish. Once the plaster has cured, it will be difficult to hide any flaws in the finish, so it's crucial to do it correctly the first time.
Rendering
Plastering by rendering entails covering a surface with a thick layer of plaster and then texturing it with a trowel or sponge. Rendering is typically applied to exterior walls to protect them from the elements and add a finishing touch of aesthetic appeal.
Rendering is covering a surface with a thick layer of plaster using a trowel or hawk. After applying the plaster, it can be textured in some ways, such as by dragging a trowel across it or dabbing at it with a sponge to create a stippled pattern. The final look can be altered by altering the finish's texture.
Rendering helps to protect exterior walls from the elements by adding a protective layer. Exterior walls can also have a decorative finish rendered on them, giving them a one-of-a-kind and aesthetically pleasing look.
You need to hire an experienced plasterer if you want a professional render. The plasterer's speed and precision are essential for creating a smooth and uniform surface. In addition, once the plaster has dried, flaws in the texture or plaster will be much more noticeable and difficult to hide.
Factor Affecting Plastering Quality
Getting a good plaster job takes practice, training, and a keen eye for detail. Plastering quality can be affected by a number of different things, such as:
Type Of Plaster
The quality of a plaster job may also depend on the kind of plaster that is used. Plaster can be made from a number of different materials, such as gypsum, cement, or lime. Depending on the situation and requirements, it may be necessary to use a specific kind of plaster.
Application
Plastering quality is highly dependent on how well it is applied. Whether floating, skimming, or rendering, the plaster should be applied uniformly and smoothly. A sloppy application process can lead to an ugly, uneven result.
Surface Preparation
The quality of the plastering can be greatly affected by how well the surface is prepared beforehand. The area must be dry, dust-free, and spotless. Before plastering, make sure all cracks, holes, and imperfections are filled.
Drying Time
Plaster quality can also be affected by how long it takes to dry. Before doing additional work on the plaster, ensure it is completely dry. Plaster can become weak and unstable if the drying process is rushed or additional layers are applied before the first coat has dried.
Mixing
Plastering quality can also be affected by how well the components are mixed. The plaster must have the right consistency, so follow the manufacturer's mixing instructions. Plaster that is uneven and brittle is the result of over- or under-mixing.
Conclusion
Plastering, the process of adding a thin layer of plaster to walls, ceilings, and other surfaces to create a consistent appearance, is an essential part of building and remodelling any structure.
It's been around for centuries because of all the advantages it provides: it's fast to install, it reinforces walls, it looks great, it lasts a long time, it blocks out noise, it won't catch on fire, and so on.
The lath or backing used to secure the plaster affects its longevity, making it more sturdy and durable than drywall.
Plastering is also convenient because it requires no sanding after installation and produces no dust during construction. It's more efficient than using other materials because you don't have to sand the wall before applying it. Cement plaster, mud and clay plasters, and gypsum plaster are just a few examples of the many sorts of materials used to create these finishes.
The use of cement plaster is common in construction and renovation because it creates uniform surfaces. Two separate processes—a "scratch coat" and a "finishing coat"—are required for optimal protection and longevity.
Plasters made from clay and mud are more cost-effective than other options because they insulate better and are less likely to crack.
Gypsum plaster, a typical building material, has better insulating characteristics than lime plaster and generates a flat, homogeneous surface on walls and ceilings.
For a more long-lasting coating, try using lime plaster, which consists of lime, sand, and water to provide a smooth, paintable, or unfinished surface.
Plastering, in conclusion, contributes much to the quality and durability of a building and has many uses for both interior and exterior coatings. Plastering is a flexible and inexpensive way to improve your home's aesthetics and practicality.
Plastering methods involve covering a surface with a thin layer of plaster to make it look smooth and consistent.
Skimming, floating, and rendering are all plastering techniques used to create a variety of visual effects. Skimming is an easy and economical technique to give a room a new look since it covers up imperfections and creates a smooth surface that is suitable for painting or wallpapering.
Skimming is best left to the pros who have the experience and training to apply the product smoothly and evenly.
Plaster is "floated" by first applying a thick coat and then smoothing it out with a float or trowel. This method is great for levelling down rough patches on interior or exterior walls.
The quality of the plastering job depends on the speed and accuracy of the plasterer.
Rendering is the process of applying a thick coat of plaster to a surface and then texturing it using a trowel or sponge so that it seems finished and professional.
This method is useful for weatherproofing and beautifying exterior walls.
Different types of plaster, methods of application and surface preparation, drying times, and mixing techniques can all have an impact on the final product.
The success of a plastering project hinges on many factors, including the plaster's composition, the surface's condition, the drying period, and the mixing procedures.
An uneven and unsightly appearance can be the result of careless application. A successful plaster job requires practise, training, and an attentive eye for detail.

Content Summary
- Plastering is an essential part of constructing or renovating any structure.
- Plastering involves covering ceilings, walls, and other surfaces with a thin layer of plaster.
- Plastering enhances the appearance of a structure and makes it look better.
- Plastering serves practical purposes like protecting the structure from the elements.
- Plastering helps in reducing noise transmission.
- Plastering has been practiced by ancient civilizations like the Greeks, Egyptians, and Romans.
- Plastering is a common method of interior and exterior finishing in modern construction.
- Plastering allows for quick refurbishment of walls, making it an alternative to drywall repair.
- Concrete membranes can be used in plastering to reduce construction costs.
- Plaster murals on walls are more robust and durable compared to dry walls.
- Plastering adds style and aesthetics to a home by highlighting its natural beauty.
- Plaster moulds can be applied to walls and ceilings to create a "Wow!" effect.
- Plastering improves the strength and longevity of walls.
- Plaster is more durable and long-lasting than drywall when properly mixed and applied.
- The choice of backing material for plaster, such as metal lath or solid backing boards, affects its durability.
- Plastering helps in noise absorption and acts as a fire retardant.
- Lime plaster, in particular, has acoustical and sound-absorbing properties.
- Lime plaster slows down the spread of fire compared to standard drywall.
- Plastering is easy to install and creates minimal dust during the process.
- Plastering does not require sanding and can be applied in less time compared to other materials.
- Different types of plastering materials offer various advantages.
- Cement plaster is commonly used in building and remodeling projects.
- Mud and clay plasters provide durable finishes and superior insulation properties.
- Gypsum plaster creates a flat, uniform surface and has better insulation than lime plaster.
- Lime plaster is widely used and offers protection against moisture and elements.
- Plastering techniques like skimming, floating, and rendering achieve different aesthetic results.
- Skimming creates a smooth, even finish on surfaces that don't require extensive repairs.
- Skimming is a fast and affordable way to update the look of a room.
- Floating is used to smooth out uneven surfaces and produce a uniform coating.
- Floating can create textured or stippled finishes for decorative effects.
- Rendering involves covering a surface with a thick layer of plaster for protection and aesthetic appeal.
- Rendering can be textured to create unique and visually pleasing finishes.
- Plastering quality can be affected by the type of plaster used.
- Proper application of plaster is crucial for achieving a high-quality result.
- Surface preparation is essential to ensure a smooth and even plastering finish.
- All cracks, holes, and imperfections should be filled before plastering.
- Sufficient drying time is necessary for the plaster to set and become stable.
- Rushing the drying process or applying additional layers too soon can compromise plaster quality.
- Proper mixing of plaster components is important for achieving a consistent and durable result.
- Over- or under-mixing can result in uneven and brittle plaster.
- Plastering requires practice, training, and attention to detail to achieve good quality.
- The choice of plastering technique depends on the desired aesthetic outcome.
- Plastering can be a cost-effective solution for interior remodeling.
- Plastering allows for the use of different decorative effects and finishes.
- Plastering materials like cement and gypsum provide long-lasting surfaces that.
FAQs About Plastering
No, it is not recommended to mix different types of plaster. Each type of plaster has a specific composition and set of properties that are designed to work best for certain applications. Mixing different types of plaster can result in an inconsistent mixture that may not adhere properly or have the desired characteristics. Therefore, it is important to use the correct type of plaster for each project to ensure a successful outcome.
Yes, plastering can be done on metal surfaces, but the surface must be properly prepared to ensure good adhesion. The metal surface should be cleaned of any dirt, rust, or other contaminants and may need to be primed with a bonding agent to help the plaster adhere.
Additionally, the type of plaster used for metal surfaces may need to be specifically formulated to accommodate any expansion or contraction of the metal due to temperature changes. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and consult with a professional if unsure about the appropriate plastering method for a metal surface.
The time it takes for the plaster to set can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of plaster used, the room's temperature and humidity, and the application's thickness. Generally, plaster takes about 24-48 hours to set and dry fully, but it may take longer for thicker layers or in high humidity or low temperatures. Therefore, following the manufacturer's instructions and allowing enough time for the plaster to fully set before attempting to sand, paint or apply any additional finishes is important.
Yes, plastering can be used for decorative purposes as it can create a smooth and even surface that can be painted or finished in various ways. Plastering techniques such as Venetian plaster or textured finishes can create unique decorative effects on walls and ceilings.
Additionally, plaster can be moulded or sculpted into intricate designs or decorative features such as cornices, columns, and arches. The versatility of plastering makes it a popular choice for both functional and decorative applications in construction and interior design.
The best type of plaster for damp areas is a moisture-resistant plaster such as cement-based plaster or gypsum-based plaster with additives that make it more moisture-resistant. These types of plaster are designed to withstand the effects of dampness and prevent mould and mildew growth.
It is important to ensure that the surface to be plastered is properly sealed and free of any dampness before applying the moisture-resistant plaster to ensure its effectiveness. Additionally, it is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions for mixing and applying the plaster to ensure its durability in damp environments.