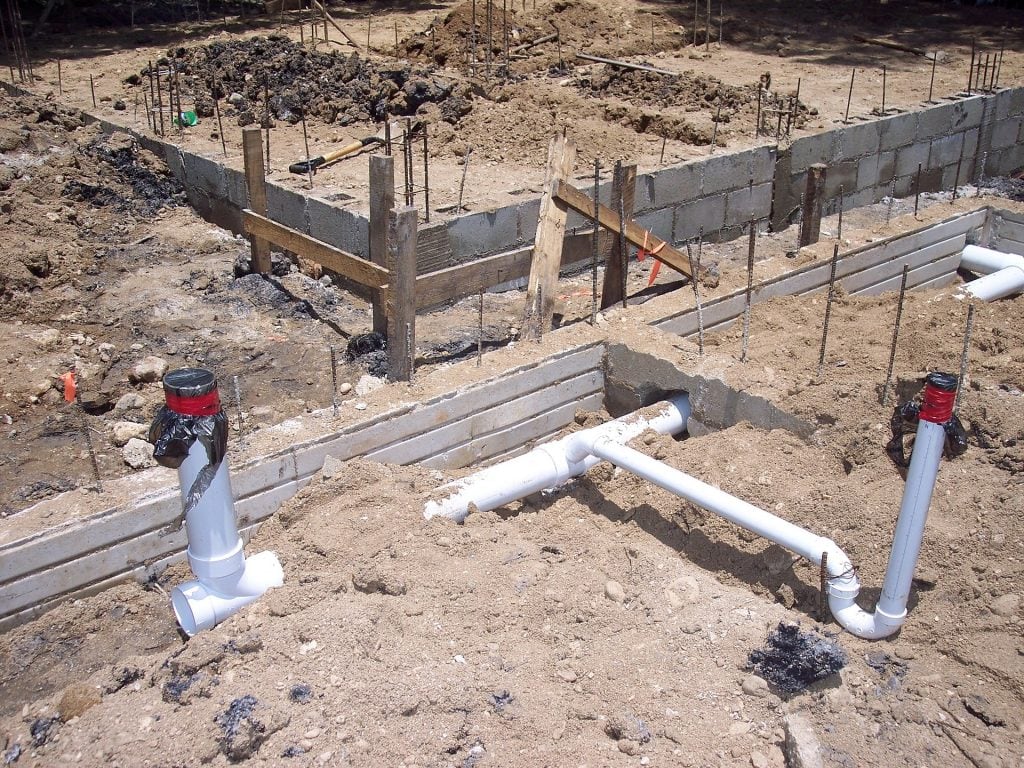
For buildings of every kind, from single-family houses to skyscrapers, picking the correct foundation is essential. A building's foundation transfers the weight of its bearing walls to the underlying soil or bedrock and prevents water seepage into the structure.
The size and kind of your project, as well as the geology, pedology (the study of soil), and other characteristics of your construction site, will all play a role in deciding what kind of foundation to choose.
Having solid foundations is essential.
The structure on top relies on the foundation below it. The foundation prevents the structure from "settling," or sinking, into the ground. Inadequate building foundations can cause structural damage or even the building to collapse.
Weight can be distributed evenly across a surface whether the foundation is shallow (going only 1 m into the ground) or deep. The most popular type of foundation is made of concrete, but steel and wood are also frequently employed.

Types of House Foundation
Basement
Basements are more common in colder regions. Basements, as opposed to crawl spaces, often provide more usable area. With or without the addition of windows and doors.
To create an underground living space that is at ground level or below, a full basement foundation typically requires digging a hole at least 8 feet deep. You will use concrete footings to construct the basement walls. These foundations need to be set 12 inches below the level of the surrounding, undisturbed soil and the frost line. Construct the walls of the foundation, then fill it in with cement and pour the beams.
A home's square footage may be increased by as much as 100 square feet if the basement is finished. Underground spaces, such as basements, are safe from both fire and the elements.
Home foundations in the Midwest, Mid-Atlantic, and Northeast must be positioned below the frost line to minimise movement during freeze-thaw cycles. They share the building's HVAC system.
If you don't have the budget for a daylight basement, which opens to the outside on at least one side, a basement will feel like a dark cavern. Avoid constructing basements in flood-prone areas. Experts advise installing a sump pump even in low-risk regions.
A residence in Australia can take advantage of basement foundations and subterranean space for parking if the local climate and water table are suitable for doing so.
A daylight basement is an attractive substitute for a full basement foundation in sloping lots because it provides a ground-level entry to the basement.
An essential step in building a new house in Melbourne is selecting a reliable builder. Check out our range of the best home design constructions at Hitch Property Constructions.
Crawl Space
The most common type of foundation is a crawl space since it may be used in any climate. They are elevated structures with sufficient basement storage. All of the home's piping, mechanicals, and maintenance can be accessed from this area. Crawl spaces can be utilised to store minor objects when they are not occupied.
There are many positives to using a crawl space as a foundation, but it does require careful planning. One of these is moisture. Crawl space goods are susceptible to mould and mildew growth because of groundwater vapour. Crawl spaces should be built with barriers that prevent the entry of moisture, unpleasant odours, mould spores, and pests.
Crawl space houses are supported by short stem walls and concrete footings. They provide an elevated area under a house that can be crawled through and is typically used to house a furnace and other mechanical systems.
In order to safeguard dwellings, crawl spaces are built below ground. You may protect your home from flooding and other natural disasters by simply elevating its foundation. You can get to the piping, wiring, and other mechanicals without any trouble. A house looks nicer when its foundation is raised. It's more cost-effective than constructing a basement from scratch.
These kinds of structures are best suited to more temperate regions. A lot of architects use them while making plans for buildings in seismically active areas.
Even while termites are less of a problem in elevated crawl space foundations, the humidity there makes it more susceptible to mould and mildew. Crawl spaces are less expensive to build than basements, but they still need regular maintenance like ensuring the walls are clear of cracks and the plumbing is not leaking.
Pier and Beam
Pier and beam construction is recommended for homes in coastal areas due to the stability it provides against soil movement, flooding, and erosion. Those prone to flooding or hurricanes are more likely to have one. Careful preparation is required since they must provide structural support while also shielding the house from water damage.
Long pillars are embedded into the ground or rock to create an effect similar to that of an ocean pier. Construction companies employ them while erecting larger, heavier houses to prevent the structures from sinking.
A soil analysis performed by a structural engineer is essential for safe construction. Construction of concrete piers calls for substantial resources, including both time and money.
Because of their low cost, pier foundations are frequently used. The house's electrical and plumbing systems can be serviced thanks to the elevated base.
Houses built on piers often have poor air circulation, which can lead to the growth of mould and the rot of wooden floors. Pier foundations have gained popularity due to their useful features. Pier foundations can be used on sloped sites, are long-lasting, and don't break the bank. They offer a more sustainable alternative for homes.
Slab
A slab foundation consists of a uniform concrete layer laid directly on the soil. The construction time and cost of monolithic bases are drastically reduced.
Slab foundations are more common in warmer areas. After excavating perimeter footings and removing and grading soil, construction crews then pour concrete directly into the ground.
Setup is a breeze. The two-foot-deep concrete beam is reinforced with wire mesh and steel rebar. Slab-built houses are low-maintenance since they lack crawlspaces.
A poured concrete slab will not have any crevices where it could collapse and damage the underlying structure. As the ground freezes and thaws in cold climes, cracks can occur in concrete, making it unsuitable for use there.
Before the concrete is poured, the drain and sewer lines must be laid. Cutting into the slab is necessary to gain access to pipes for plumbing or sewage.
Despite these drawbacks, slab foundations are often chosen, especially for development projects due to its low cost and ease of construction. In addition to being an effective insulator, they also deter animals from making their homes directly under people's.
Wood Foundations
In the 1960s, wooden subfloors were all the rage. Preservative-treated wood is used because it resists decay and is simple to set up. Since they don't necessitate costly and time-consuming processes like concrete pouring and brickwork, wood foundations are both quicker and cheaper to instal.
Contractors can insulate this type of foundation to keep the crawlspace toasty and cut down on draughts. In the Egyptian pyramids dating back 6,000 years, archaeologists have uncovered beams made of wood from Cyprus.
Cypress, redwood, and cedar are three examples of insect- and mold-resistant woods. Those types of wood are quite costly, therefore the timber business has developed methods to treat cheaper varieties so that they behave similarly. They may not be as durable as concrete, and only work on dry soil.
Who Designs Foundations for Homes and What is Involved?
An engineer is usually consulted to design house foundations that are appropriate for the soil type, slope of the land, and expected loads. At HP Constructions, we have the best home constructions selection to make your house a dream come true.
The soil report is necessary for the engineer to design the foundation of your house. The bearing capacity and moisture responsiveness of the soil are evaluated in the soil report. Gathering soil samples from various locations is an integral part of the soil test (referred to as bores). In accordance with Australian standard 2870, these samples have been examined in a laboratory and categorised.
Foundational factors such as depth, steel grade, and concrete strength are all established by soil classification.
All buildings require a solid, natural base. Pure, unaltered soil. The foundation may need to be dug into the earth if the existing soil is thick or if the area has been filled in with unregulated material. The piers in Melbourne tend to be uninteresting.
Strength of concrete is a topic covered by MPA. The MPA of the concrete must be between 20 and 25 for the slabs. Concrete with a compressive strength of 32 MPa is suitable for thicker slabs. Adding steel to concrete makes it stronger and more rigid. A steel mesh reinforces the structure.
To attain the desired slab stiffness, engineers typically request mesh by size. Square mesh is indicated by the notation SL62, SL72, SL82, SL92, and SL102. The diameter of the bar is the first number. The number following the colon denotes the distance between the bars. 7 mm bars at a 200 mm pitch characterise SL72. Strength-rated mesh is superior.
A slab's strength is increased when steel is used. The use of two mesh layers, as opposed to one, can make slabs far more robust.
The depth of the concrete rib on the slab will also be decided by the soil report. Stronger slabs can be built on deeper foundations.
It is fairly uncommon for a single home to employ all four of these foundation types due to the complexity of modern design and the challenges presented by atypical or unconventional building locations.
How Much are House Foundations?
It is possible to be charged on a per-square-meter basis for foundations. However, there is more to laying foundations than just picking the right sort of foundation; there are other factors to take into account in the planning stages, and we can go over those with you. Further, we can assist you in establishing your footing for future accomplishments. Common examples include sealing, heating, and drainage.
It is more cost-effective to build a house with all the necessary components incorporated from the start. Looking for the best home constructions? Look no further! Hitch Property Constructions has the ultimate list of home designs for you to choose from.
Can You Soil Test Prior to Purchasing Land?
Before purchasing a lot, a soil test must be performed. That's a matter of contract. You'd need a good cause to pull out of a purchase that included a soil test as a contingency. A soil test is defined as one that satisfies the requirements of your purchase agreement. Problematic soil, rocks, and contamination. There is a design and plan for a foundation that can be used in any soil, albeit it will be more expensive than using regular dirt. Talk to an attorney if your worries persist.
Your project's size, location, and geotechnical constraints will determine whether shallow or deep foundations are required. There may be subtleties in the foundation type. The safety and durability of a building rest entirely on the foundation's choice.
Conclusion
The bearing walls' weight is transferred via the foundation to the soil or bedrock below. Concrete is the material of choice for most foundations, however steel and wood are also widely used. It is usual in northern climates to dig a hole at least 8 feet deep for a basement. In cases when a full basement foundation would be too costly to dig, a daylight basement is a great alternative. Accessible from here are high-rises with spacious basements for storing personal belongings.
The groundwater vapour in a crawl area might cause the goods to mildew and mould. These kinds of buildings are more comfortable in milder climates. A concrete slab is a flat concrete layer that is placed directly on the ground. Because of its many advantages, pier foundations have becoming increasingly common. Savings in both time and money during the building process of monolithic bases are substantial.
As slab foundations are more likely to develop cracks in colder climates, they are more commonly used in warmer regions. House foundations should be designed by an engineer to account for the soil type, land slope, and anticipated loads. Woods like cypress, redwood, and cedar are resistant to insects and mildew. Steel reinforcements in concrete improve the material's durability and stiffness. Is a Soil Test Required Before Buying Land?
A soil test is required prior to the purchase of any land. When it comes to a building's stability and longevity, the decision of its foundation is crucial. A foundation layout and strategy exist, and it may be implemented in any type of soil.
Content Summary
- The size and kind of your project, as well as the geology, pedology (the study of soil), and other characteristics of your construction site, will all play a role in deciding what kind of foundation to choose.
- Having solid foundations is essential.
- A daylight basement is an attractive substitute for a full basement foundation in sloping lots because it provides a ground-level entry to the basement.
- An essential step in building a new house in Melbourne is selecting a reliable builder.
- The most common type of foundation is a crawl space since it may be used in any climate.
- They are elevated structures with sufficient basement storage.
- There are many positives to using a crawl space as a foundation, but it does require careful planning.
- In order to safeguard dwellings, crawl spaces are built below ground.
- It's more cost-effective than constructing a basement from scratch.
- Construction of concrete piers calls for substantial resources, including both time and money.
- The soil report is necessary for the engineer to design the foundation of your house.
- The bearing capacity and moisture responsiveness of the soil are evaluated in the soil report.
- However, there is more to laying foundations than just picking the right sort of foundation; there are other factors to take into account in the planning stages, and we can go over those with you.
- Before purchasing a lot, a soil test must be performed.
- You'd need a good cause to pull out of a purchase that included a soil test as a contingency.
- A soil test is defined as one that satisfies the requirements of your purchase agreement.
- There is a design and plan for a foundation that can be used in any soil, albeit it will be more expensive than using regular dirt.
- There may be subtleties in the foundation type.
- The safety and durability of a building rest entirely on the foundation's choice.
FAQs About Home Construction
- The following are the best foundation types for a house,
- Isolated Column Footing.
- Basement Foundation.
- Slab Foundation.
- Wall Footing Foundation.
- Pile Foundation.
A house foundation is the load-bearing portion of the structure, typically built below ground. The foundation you choose boils down to personal preference and budget.
Foundations are generally made of sturdy materials that can keep the home standing even during earthquakes and cyclones. As a result, they are often built of concrete, the strongest building material. Concrete foundations are either poured into place or placed in excavated holes.
Overall, concrete slab house foundation are the most common type. These foundations are made from poured concrete – usually between four and eight inches deep – and reinforced with steel bars called rebar.
slab foundation
The most common type of foundation is a slab foundation. It is also one of the most budget-friendly and straightforward to build. As the name suggests, it is a foundation of slab concrete that is around 6 to 8 inches thick. The concrete is poured into a gravel mixture in the soil's surface.