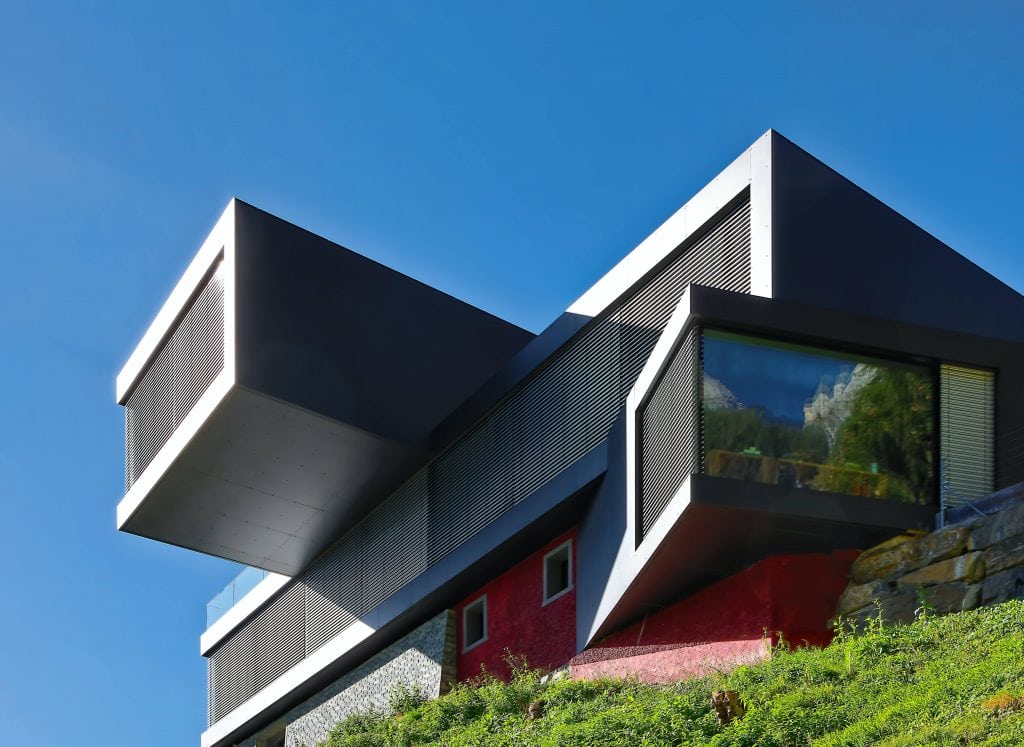
Buildings intended for commercial use are constructed and furnished otherwise than single-family dwellings. Energy efficiency, productivity, and human interaction are all factors that architects and builders must take into consideration. Pretend for a moment that you are one of these experts. You might be familiar with several types of shading arrangements, such as horizontal and vertical blinds, egg crates, and honeycombs.
The outside of a business establishment needs to be sturdy and safe from the elements. There must be insulation from heat, sound, and flames. The complex's kind and size, as well as local planning restrictions, airflow, daylight penetration, wall-to-window ratio, shape, height, and visibility, are all taken into account. The company's mission and values should be reflected in the brand. As a result of these demands, cutting-edge materials and manufacturing processes have emerged.
A building's exterior and all of its visible faces are collectively known as its "facade," which is derived from the Italian word "facciata." It is customary to confine the term's application to the visible face of a structure.
It is, together with the roof, one of the most crucial parts of a building since it protects the interior from the elements. Rain, snow, wind, frost, and the sun are all examples of such phenomena.
That's why it's crucial to pick a facade system that can shield you from danger while also helping you save money on utilities, cut down on repairs, and feel more at ease in your home.
Here we break down the many facades and outside walls that are in use today, along with some key aspects of each.
Hitch Property Constructions has the best range home facade renovations.
What is a facade?
The facade is the visible part of a building. A nice outer shell keeps the inside safe. Facades shield us from the cold in the winter and the heat in the summer, as well as the elements and fire. Enhancing the visual appeal of our structures, facades are an essential element. All of these qualities can be seen in the facades: rhythm, balance, proportion, innovation, and a sense of adventure. To be successful, an architectural design must strike a balance between the two. The emergence of cutting-edge technologies has allowed for innovative approaches to building skins. When it comes to realising an architect's design and providing a high-performance shell for end-users, architects and manufacturers are always on the lookout for novel façade solutions.
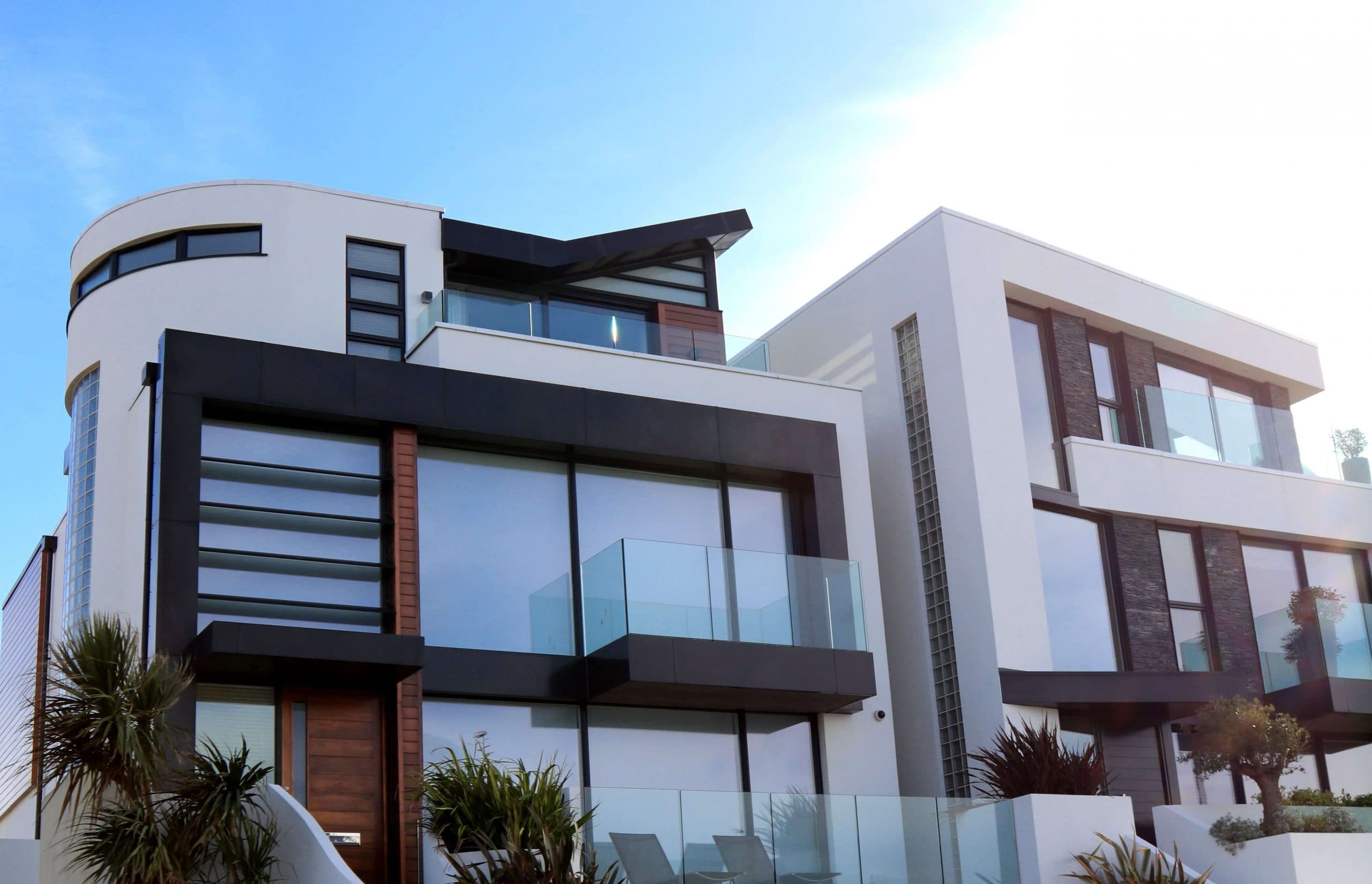

Types of facades for buildings
Lightweight facade
This façade style is linked to the building's resistive construction rather than being an integral part of the building. Since the lightweight facade does not contribute to the building's overall stability, it must be planned to withstand the loads that stress its components.
Material used in cladding includes glass and metal among others.
The two most common methods of constructing lightweight facades are curtain walls and panel facades. The framework does not interrupt the façade's continuity in a curtain wall, but it does in a panelled facade.
Two major advantages of the lightweight facade system are the ease with which it can be installed and the amount of natural light that can enter the building.
Lightweight facades are more expensive to maintain and offer worse heat and sound insulation compared to heavier facades.
Medium- to high-rise office buildings are typically the sites where this type of facade is installed.
Heavyweight facade
The name of this style of facade alludes to the fact that its components often weigh quite a bit. The average weight of the facade, including both the solid and hollow components, must be larger than 100 kilogrammes per square metre for the facade to be considered a heavyweight facade.
Facades in this group can range from load-bearing to self-supporting, with or without an air chamber, depending on the thermal insulation needs of the building.
Prefabricated
Prefabricated modules are typically used in this type of facade, which is then constructed on site or linked together. These facades are manufactured in highly mechanised factories using standardised components. Panels of wood and concrete are commonly used in their construction.
It's easy to instal, doesn't cost as much as other systems, and can be put up quickly, so that's why most people choose to use this type of façade. The disadvantages include less freedom in terms of design and a base level of effort that must be met before it can be considered.
Prefabricated facades are commonly found in large retail malls and manufacturing facilities.
Traditional
Traditional facades use common construction materials like brick, stone, wood, ceramics, rendering, and other comparable products.
The benefits include lower total cost, quicker installation time, and simpler building requirements.
However, the lack of air chambers and insulation in conventional facades makes them less effective in preventing the movement of heat and sound, and hence less likely to result in savings on energy bills.
ETI Systems
Installing plates of insulation material around the perimeter of a building is a key component of ETI (External Thermal Insulation) systems. Mortar is used to coat these plates, and they are attached to the walls holding them in place using adhesive or mechanical means.
After that, the system is finished with cladding or another finish that complements the building's design.
The insulation part of an ETI system typically makes use of expanded polystyrene, extruded polystyrene, graphite expanded polystyrene (EPS-G), and mineral wool (MW).
The ETI technology reduces the risk of thermal bridging and condensation formation due to its insulating layer.
As there are no out-of-pocket expenses required to implement a framework system, this option provides adequate value for the money.
Rainscreen cladding
A ventilated facade consists of the load-bearing wall, an insulation layer, and the cladding. These materials, also known as rain-screen cladding or ventilated facade, are fastened to the building via a supporting structure.
The most noticeable difference between this system and the ETI system is the air cavity that is included between the load-bearing wall and the cladding material.
Since the air gap is responsible for many of the advantages of rainscreen cladding, it is usually the most cost-effective option to instal this system, despite its greater complexity and higher price tag.
Because of the "chimney effect" occuring within the air cavity, hot air is driven upwards and out of the building via the top of the façade. Natural convection keeps the air constantly replenished during the warmer months, keeping individuals from overheating. During the colder months, however, the air does not circulate outside as much and instead remains within the house. Due to less heat loss, less fuel is needed to maintain a comfortable interior temperature.
Since the structure is subjected to fewer temperature variations, the appearance of cracks and fissures is reduced, and rain-screen cladding provides an extra layer of protection against condensation and water infiltration. These advantages result from the use of rain-screen cladding.
These are just some of the many reasons why vented rain-screen cladding is the most effective external façade technology on the market today.
Types of Facades for your Commercial Complex
Steel facade
Almost all office buildings constructed in the last few decades include light steel infill walls. Concrete and steel framing systems are used in place of the more conventional inner leaf structure of blocks when constructing new buildings. This common feature allows for the easy incorporation of different facade systems into the infill walls, which is a huge time saver.
These buildings are easy to erect and can supply C sections of any needed length. They are sturdy enough to handle the load of any cladding system that is fastened over them and can withstand the effects of wind pressure.
Curtain-wall facade
Typically, curtain walls are coated with metal or glass. It has a solid framework underneath it. A big tiled fascia or stone veneer attached to the exterior of your building can achieve this effect. Curtain wall facade components are manufactured in factories. Panels are made from them in a factory by skilled personnel. On-site, they set up a system of interlocking units. Glazing panels that are installed as a unit. Curtain walls are often built on-site and then given a final adhesive coating.
The height between stories, mode of transport, and location of installation all influence the size of unitized panels. Most panels have a width of 1.5 m and a height of 4.2 m. Curtain walls can withstand the elements and provide natural light, shading, and insulation.
Aluminium composite panel (ACP) facade
Aluminium composite panels, abbreviated ACP, are a type of flat panel consisting of a thermoplastic core sandwiched between two sheets of aluminium. Because of their low weight without sacrificing durability or strength, architects and builders frequently employ them for outer walls. ACP can also be designed in a wide variety of imitation patterns and colours, both metallic and nonmetallic.
You may make them look like marble or wood, depending on your preference. The adaptability of ACPs extends beyond cladding; they can also be utilised as partitions and artificial ceilings. They're available in many different thicknesses and have many different possible surface treatments. They're malleable, so you can give them any shape you wish, from simple to elaborate.
Planning for Melbourne home facade renovations? Look no further! Hitch Property Constructions has you covered.
Double-skin facade
Two panes of glass are used in a double-skin facade, with the space between them serving as a hollow. They are useful for commercial properties that want to reduce their energy consumption. Construction workers instal cavity shading. In order to facilitate maintenance and accessibility, builders will often instal pathways.
Double-skinned outside walls reduce heat loss and gain. Heat loss during the winter is minimised via passive solar gains. Connect the ventilation of the cavities to the rest of the building's infrastructure. Because of this, solar-heated air is brought inside. The natural ventilation is enhanced and the need for artificial heating is decreased. In the summer, this space allows hot air to escape. As a result, less energy is required to chill the structure.
Brick slip facade
A brick slip façade is an alternative to a standard brick facade that uses thin bricks instead of whole bricks. The panels are installed by the construction crew on steel studs or composite panels. Due to the elimination of mortar, the overall weight of the structure can be reduced, and the building process can be completed in a fraction of the time. There is no one "right" way to stack brick slips.
Some designs feature odd window forms or vertical lines or ribbons. Because of their porous nature, brick slips are not particularly resistant to climate change. Therefore, you should pay some care to the backing material. Composite panels, for example, provide structurally superior protection against heat and the environment.
Steel and glass facades
Steel and glass are commonly used for the outer skins of high-rise buildings. Steel columns are typically used to support glass facades. Everything rests on the building's external frame, which provides structural support. Stainless steel and hollow steel pieces are common building materials for this type of facade.
Precast concrete facade
Precast concrete panels, because of how quickly they can be installed, are a great option to employ when the construction schedule is tight. The production process is easy to understand. After workers cast concrete into reusable moulds, the mixture is allowed to cure in a controlled setting. Trucks deliver the materials to the job site, where they are positioned by means of heavy equipment.
Main Questions when Choosing the External Cladding Systems
Whether you're interested in front panels, siding, bark beetle, plaster decoration, etc., the number of possible finishes is nearly endless. If you're looking for the most cost-effective approach to spruce up the exterior of your home, you should still ask yourself these three questions first. The answers to these three questions, as well as a photo gallery showcasing some of the most popular decorating techniques, will no doubt be of interest to you as you consider options for the design of your home's external walls.
What facade finishing materials do you like?
Although it is said that substance is more essential than form, the facade of your home is the first thing that visitors and neighbours alike will notice. Facing materials set the tone for the rest of the design, including the interior, so it's crucial to choose something that reflects your own personal interests and creates a unified design across the home. For this reason, picking the right facing materials is crucial.
Your home's kerb appeal and courtyard design work together to produce what's called a "attractive impact." This is why an outsider's view of your residence will be different than your own. It is normal practise to have a real estate agent market your house when the time comes to sell it, thus it is crucial that all of the information presented be correct.
The complexity of the service for which you are ready to go?
The materials you choose for your facade should be evaluated not only for their visual attractiveness, but also for the amount of upkeep you are ready to put in to keep it looking fresh. Some cladding materials require more upkeep than others, but there are many options to choose from. If yours doesn't, you may want to look into finding something else that will do the job.
Consider a tree in your yard as an illustration. Modern timber facades can be constructed to require only the right amount of time and effort to maintain, in contrast to the traditional cladding material, which has a reputation for demanding an extraordinary lot of both. The natural beauty of dried wood makes it a prefered building material for today's homes. With its natural feel, very little work is necessary in terms of the content, which leads to long-term cost savings.
What is the environment?
The sun, wind, and noise levels are three environmental issues to think about before designing your outside wall structures. The sun is an obvious consideration; if your house is facing north, it will receive a lot of direct sunshine, and you should use building materials that can withstand this. The placement of walls, windows, and doors can greatly affect the amount of air that can circulate through a home, making it more comfortable to live in during the warmer months. The wind may be less reliable than the sun, but it's still crucial to plan accordingly. Electricity costs will catch you off guard every month.
A thing's aural quality is also very significant. Do you happen to reside in a particularly noisy locale? Brick exterior walls (and interior walls, if you can afford it) are good at dampening sound because of their large thermal mass and providing other insulation benefits. This is a potential route worth considering.
Installing a chimney made of a different material, making a pattern with bricks or tiles used for the outer face, or selecting a style more in line with nature are all straightforward ways to alter the appearance of the building's exterior walls. Decorating the outside of buildings with vertical gardens is becoming increasingly trendy.
Common Facade Systems and Materials
Masonry veneer
In the state of Indiana, brick has shown to be a reliable and effective building material. On practically every project, we evaluate brick against alternative materials for price, functionality, and visual appeal. Brick wins because of its durability, adaptability, and familiarity. Our default wall types include brick veneer, air gap, 3" rigid insulation, and backup wall. This layout is simple to understand. It's reasonably priced, sturdy, and insulated, and it has a design that's uniquely at home in the Midwest. Like any material, bricks can be made in a variety of sizes, hues, and finishes to suit your needs. You can use brick with or without stone and CMU. Most of the buildings in our area have a masonry exterior.
Metal Wall Panels
Metal panels could be a suitable exterior finish material, but this would depend on the Owner, the nature of the project, and the available budget. These types of wall systems are commonly found in contemporary buildings. Panels made of metal can be customised in a number of ways, both aesthetically and functionally. This stuff is pricey and might cause delays in a project. Scheduling and building inclosure are two areas that may be impacted by field verification and panel production. A significant portion of the price of using panels can be avoided by sticking with standard sizes.
The R-value of metal walls that have been adequately insulated is greater than that of encased insulation. Extra framing for the façade may be required, depending on the system and the backup wall. Although some suppliers might tell you otherwise, sheathing is essential for weatherproofing and finishing the inside of your building.
EIFS
Insulating and decorative, EIFS is a veneer system. The material used is known as stucco. It is possible to fool people with this content. EIFS looks just like stone to the untrained eye. EIFS can be made to look like brick or metal siding. System components include spray-on or troweled-on finish and stiff insulating board. The material is applied as a liquid, making it easy to carve intricate designs onto buildings. It's lightweight and requires less structural support than alternative façade technologies. Per square foot, EIFS is the most cost-effective insulation option.
Unlike other building materials, EIFS doesn't hold up well over time. If you have hard insulation and then a thin layer of EIFS, the EIFS will be degraded quickly. Lawnmower rocks are a known source of flat tyres. The surfaces might discolour or get stained with time. For these reasons, EIFS is used to safeguard the building's upper components.
Cementitious (Fiber-Cement) Siding
This technique is used for both residential and non-residential construction. There has been a rise in the use of cementitious siding on commercial structures. The material can be purchased as panels or shake-like panels, both of which mimic traditional wood siding. This facade is long-lasting and requires little upkeep. Finished ahead of time or in the field. It can be challenging to consistently insulate this lightweight material. When compared to EIFS, it saves money and lasts longer. Proper insulation is crucial.
We have a huge range of home facade renovations Melbourne at Hitch Property Constructions.
Precast concrete
Facades can occasionally be made out of precast concrete panels. Multiple applications exist for these panels. As a wall and structural system, they help get a building up and running faster. The aesthetic of precast concrete panels can be altered to fit the needs of the project. Maintaining size consistency and simplifying design elements might help you compete. The price goes up when there are a lot of different sized panels or irregular ones. These panels are manufactured, shipped, and set up by professionals. Until the roof is constructed, they are braced. Panel fabrication might take up to six months, but erection is quick. The value it adds to a project can be measured against that of competing systems.
Facades enhance the visual appeal of a building by showcasing design elements and establishing a sense of rhythm and proportion. Facades are designed by architects and builders to be both functional and aesthetically pleasing. You may now provide your customers with high-performance facades thanks to advancements in technology.
Conclusion
A facade of what? A building's facade is its outside appearance. Because it keeps the interior safe from the weather, it is an essential component. You may reduce your utility bills, spend less on repairs, and feel safer in your home just by updating the facade. This type of façade is not an intrinsic element of the structure itself but rather is connected to the resistive construction.
In addition to being more costly to maintain, lightweight facades are also less effective in preventing heat loss and sound pollution. The term for this facade style references to the fact that its parts can be extremely heavy. One of the main features of ETI (External Thermal Insulation) systems is the installation of plates of insulation around the perimeter of a structure. Because of its insulating layer, ETI technology lessens the possibility of thermal bridging and condensation. An additional safeguard against moisture buildup and water intrusion is provided by rain-screen cladding with vents.
Instead of the more common inner leaf structure of blocks, concrete and steel frame systems are utilised. Consequently, various facade systems can be simply integrated into the infill walls. Facades constructed using aluminium composite panels (ACP) have a thermoplastic core between two sheets of aluminium. To lessen the effects of temperature swings, outside walls are often double-skinned. Reduced heat loss in the winter is achieved by the use of passive solar gains.
Slips made of brick are not particularly resistant to climate change since they are permeable. When time is of the essence during building, precast concrete panels are a good choice. To outsiders and curious neighbours, your home is immediately recognisable by its outside. Materials used for facades may serve as inspiration for the interior decor. These days, timber facades can be built to last for decades with no upkeep.
How much air a house can circulate is heavily dependent on its layout, especially its walls, windows, and doors. Use sun-resistant supplies if the northern exposure of your home is a need. Because of their high thermal mass, brick exterior walls are excellent in reducing exterior noise. Depending on the specifics of the job, metal panels might make a good external finish. Depending on the system and the supporting wall, additional façade framing may be necessary.
Brick and metal siding imitations are possible with EIFS. Some lawnmower rocks may fade or become stained with time. Exterior insulated finish system (EIFS) is utilised to protect the upper parts of the structure. Cementitious siding, often known as fibre cement, is more cost-effective and durable. Panels made from precast concrete can be customised to meet specific job requirements.
Content Summary
- The outside of a business establishment needs to be sturdy and safe from the elements.
- A building's exterior and all of its visible faces are collectively known as its "facade," which is derived from the Italian word "facciata."
- That's why it's crucial to pick a facade system that can shield you from danger while also helping you save money on utilities, cut down on repairs, and feel more at ease in your home.
- Here we break down the many facades and outside walls that are in use today, along with some key aspects of each.
- The facade is the visible part of a building.
- The two most common methods of constructing lightweight facades are curtain walls and panel facades.
- Installing plates of insulation material around the perimeter of a building is a key component of ETI (External Thermal Insulation) systems.
- These materials, also known as rain-screen cladding or ventilated facade, are fastened to the building via a supporting structure.
- Almost all office buildings constructed in the last few decades include light steel infill walls.
- Double-skinned outside walls reduce heat loss and gain.
- Connect the ventilation of the cavities to the rest of the building's infrastructure.
- A brick slip façade is an alternative to a standard brick facade that uses thin bricks instead of whole bricks.
- Everything rests on the building's external frame, which provides structural support.
- Although it is said that substance is more essential than form, the facade of your home is the first thing that visitors and neighbours alike will notice.
- For this reason, picking the right facing materials is crucial.
- The sun, wind, and noise levels are three environmental issues to think about before designing your outside wall structures.
- Panels made of metal can be customised in a number of ways, both aesthetically and functionally.
- Extra framing for the façade may be required, depending on the system and the backup wall.
- Lawnmower rocks are a known source of flat tyres.
- For these reasons, EIFS is used to safeguard the building's upper components.
- There has been a rise in the use of cementitious siding on commercial structures.
- Precast concreteFacades can occasionally be made out of precast concrete panels.
- The aesthetic of precast concrete panels can be altered to fit the needs of the project.
FAQs About Facade
Here are six types of modern facade design to consider for your next project.
- Ceramic facades. ...
- Stone composite panels. ...
- Precast concrete panels. ...
- Natural stone panels. ...
- Closed cavity facades. ...
- Green facades.
The definition of a facade is the front of a building facing a public space or an artificial front or appearance by someone. An example of facade is the front of the local mall. An example of facade is the putting on of a smile when really feeling quite upset.
House façades refer to one exterior side of a house – typically the front. The word “façade” is a French word, meaning “frontage” or “face”. Pronounced “fa'saad”, it's one of the most important parts of your home design.
Façade, by definition, is the face of a building. It is what you can see from the exterior that protects the interior. Façades are an integral part of the building shell – keeping us humans warm in the winter and cool in the summer, while also providing a barrier from outside elements and even fire in some cases.
A façade refers to one side, usually the front, of a building. It is an integral piece to the overall design of a building. It provides the opportunity to create a personality and character to a building.