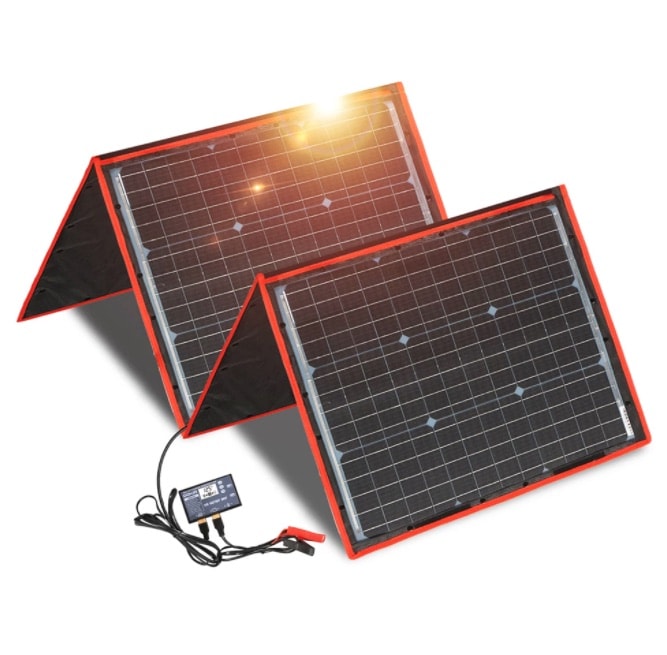
Have you thought about installing batteries alongside your solar panels? Whether you’re setting up for an off-grid cabin or adding battery backup for your grid-connected home, designing your DIY battery bank is a straightforward process.
However, if you’re unfamiliar with the process, it may seem overwhelming at first. This guide walks you through the basics, so you can confidently start your DIY solar battery project. With renewable energy becoming more affordable, the interest in creating DIY solar panels and battery banks has surged.
People take on these projects for various reasons—whether it’s saving money, experimenting, or simply the challenge. This article will guide you step-by-step on how to create your own battery bank for your solar panels.
Let’s Get Straight To The Point
Installing a battery bank alongside solar panels allows you to store energy for use when sunlight isn’t available, making it essential for off-grid setups or grid-connected homes. You can either buy a battery bank or build one yourself.
The DIY approach can save money and offers learning opportunities, though it requires careful planning. This guide walks through the basics of choosing between lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries, calculating your power load, and assembling a DIY solar generator with key components like portable solar panels, a charge controller, batteries, and an inverter.
Proper installation, including adding a junction box and selecting the right charge controller, ensures the system runs efficiently. With a few final tips on maximizing sunlight and cooling, you can create an effective and clean energy solution for your home.
What Are the Benefits of Solar Panels with Battery Banks?
Solar panels generate electricity during the day, but without a battery bank, this energy cannot be stored for use at night. A battery bank is essential for storing this energy, so your solar system continues to power your home even when the sun isn’t shining. Below, we’ll explore different types of batteries, how to build your own battery bank, and the advantages of using one.
Types of Batteries for Solar Panels
When building a DIY battery bank, you generally have two choices: lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: These are the more traditional choice. They are cheaper but less efficient and have a shorter lifespan.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These are more expensive but offer longer lifespans, higher efficiencies, and greater energy density.
Many opt for lithium-ion batteries due to their superior performance, but lead-acid batteries can still be a viable budget-friendly option.
Should You Build or Buy a Battery Bank?
You have two options for adding a battery bank to your solar system: buying a pre-made bank or building one yourself. Buying a battery bank will save you time but increase costs, especially if you hire a professional installer. On the other hand, building a battery bank requires more time and effort, but it can save you money in the long run. If you’re unsure about your electrical skills or need accurate energy calculations, hiring a professional might be the safer choice.
How to Build a DIY Solar Generator
A solar generator collects energy from the sun and converts it into usable electricity for your appliances. Building a DIY solar generator is an excellent way to learn about renewable energy and save money. Plus, you get to customize it according to your needs.
Here are the three main functions of a solar generator:
- Harvest solar energy: Capture sunlight using solar panels.
- Store energy: Use batteries to store the captured energy.
- Convert energy: Use an inverter to convert the stored energy into usable electricity.
Let’s dive into the essential steps and components required for building a DIY solar generator.
Step 1: Calculate Your Power Load
Before anything else, calculate how much power you consume daily. This calculation is essential because it will determine the size of your battery bank. You can estimate your power load in two ways:
- Use historical data: If you’re already connected to the grid, check your electricity usage over the past year, then divide by 365 to get your daily average.
- Tally appliance usage: If you’re off-grid, list all your electrical devices and calculate their combined wattage. Then, estimate how long each appliance runs daily to determine your total daily power consumption.
Accurate calculations are vital because they inform the size of your battery bank and solar system.
Step 2: Gather the Essential Components
You’ll need a few essential components to build your solar generator.
- Portable Solar Panels: Choose portable or foldable solar panels, which are rugged and compact—perfect for outdoor use.
- Solar Charge Controller: The charge controller regulates the flow of electricity from the panels to the battery, preventing overcharging. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers are the most efficient choice.
- Battery: Lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries store the energy for future use.
- Inverter: Converts DC (direct current) electricity from the battery into AC (alternating current) electricity that your appliances can use.
- Case: A protective case keeps your generator components safe from dust and moisture.
With these parts in hand, you’re ready to start building.

DIY Solar Generator Building Process
Step 1: Plan and Build a Frame
Start by drafting a plan for your solar panel and battery bank. Choose a sturdy but lightweight material like plywood for the frame. This frame will house your solar panels and batteries.
Step 2: Assemble the Solar Panels
After gathering the materials, it’s time to assemble the solar panels. The most expensive part will be purchasing solar cells, but it’s still cheaper than buying a commercial solar panel system. You can find various templates and instructions online to help guide you through the process.
Step 3: Choose the Right Inverter
You’ll need an inverter to convert the DC electricity stored in your battery into AC electricity. Choose an inverter based on the power load you calculated earlier. It’s essential to pick one that can handle your maximum energy use.
Step 4: Solder the Wiring
Next, solder the wires connecting your solar cells. This step requires patience and precision. Connect each cell’s positive and negative terminals using equal amounts of wire. Once all the wires are connected, check the current to ensure everything is working correctly.
Step 5: Power Up Your System
After connecting all the components, it’s time to power up your system. Start by connecting the solar panel to the charge controller, then attach the battery, followed by the inverter. Now, your solar system should be generating usable electricity!
Step 6: Install a Junction Box
A junction box is essential for preventing reverse current flow, which can damage your solar panels. Most modern charge controllers come with a built-in backflow preventer, but if yours doesn’t, you can install one in the junction box. After this, your solar panel system will be ready for use.
Charge Controllers and Their Importance
A charge controller is a critical component for managing the flow of electricity from your solar panels to your battery bank. It prevents overcharging, which can damage your batteries. There are two main types of charge controllers:
- Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Controllers: These are more affordable but less efficient.
- Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Controllers: These are more expensive but significantly more efficient at converting solar power into usable electricity.
When choosing a charge controller, calculate the wattage of your solar array and the voltage of your battery bank to determine the required amperage. The ideal charge controller should handle about 20–25% more current than your system produces.
For instance, if you have a 4,000-watt solar array and a 48-volt battery bank, divide 4,000 by 48 to get around 83.3 amps. In this case, you would choose a charge controller rated at approximately 100 amps.
Final Steps and Tips
Now that your DIY battery bank and solar generator are assembled, you’re ready to start generating clean, renewable energy. Here are a few final tips to ensure your system operates smoothly:
- Maximize Sunlight Exposure: Position your solar panels in a spot where they receive the maximum amount of sunlight each day.
- Install a Ventilator: If your solar generator is enclosed in a case, consider adding a small fan or ventilator to keep the system cool.
- Monitor Your System: Regularly check the charge levels in your battery and ensure that the charge controller is functioning correctly.
Conclusion
Creating a DIY battery bank for your solar panels is not only possible, but it’s also a highly rewarding project. By building your own system, you gain valuable knowledge about renewable energy and save money. Whether you opt for lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries, ensure that your components are correctly sized for your power needs.
With the right planning and tools, you can enjoy the benefits of a solar-powered system that provides clean, silent energy. So, why not take the leap and start your DIY solar journey today?
FAQs About Solar Panels
What Batteries Can Be Used For Solar Panels?
The four main types of solar batteries are lead-acid, lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium, and flow batteries. Lead-acid batteries have been around for the longest and are known for their low prices and reliability, but they require regular maintenance.
How Many Solar Batteries Are Needed To Power A House?
A 400 amp-hour 6-volt battery can provide around 2.4-kilowatt-hours of power. A three-day battery bank planned to provide 90 kilowatt-hours of electricity to an average American household. The previous example battery can provide2,4 kilowatt-hours, while 38 batteries would be needed.
Can I Connect A Solar Panel Directly To A Battery?
A solar panel can be connected directly to a 12-volt car battery but must be monitored if it’s more than 5 watts. Solar panels rated higher than 5 watts must not be connected directly to a battery but only through a solar charge controller to protect against over-charging.
How Many Batteries Are 5000 Watts?
You will need at least one 450-500 12V battery or two 210 12V batteries to supply 5000 watts of power for 30-45 minutes. If you’d like an hour of 5000 water of power, you’ll need a 750ah 12V battery.