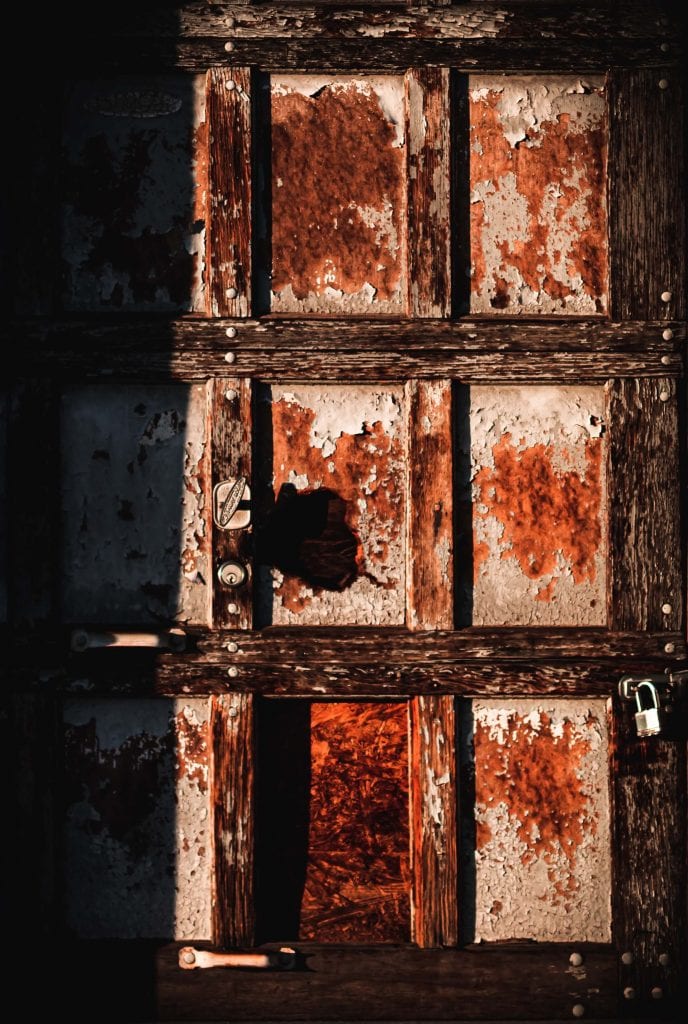
Wood rot is likely affecting the house's wooden mouldings. The deterioration may be visible, concealed, or painted over. Wood that has rotted must be fixed or replaced so that moisture, air, and insects are not allowed to enter the structure.
Any wood in a house is susceptible to wet or dry rot. Warning signs include wood that has rotted at the door, trim, window sill, floor, window sill, or column. Once a fungal infestation has started, it can't be stopped. The bad news is that replacing damaged wood is a pain and can be quite costly. Wood that isn't supporting the building almost never needs to be replaced. To fortify the vulnerable spot, try using simple products.
Wood rots because fungi thrive in damp environments. Fungal decay isn't limited to rotting wood. Both the rotted and unrotted wood must be repaired for the fix to last.
At Hitch Property Constructions, we offer timber repairs work from simple timber repair to almost new structures, renovations, and extensions.
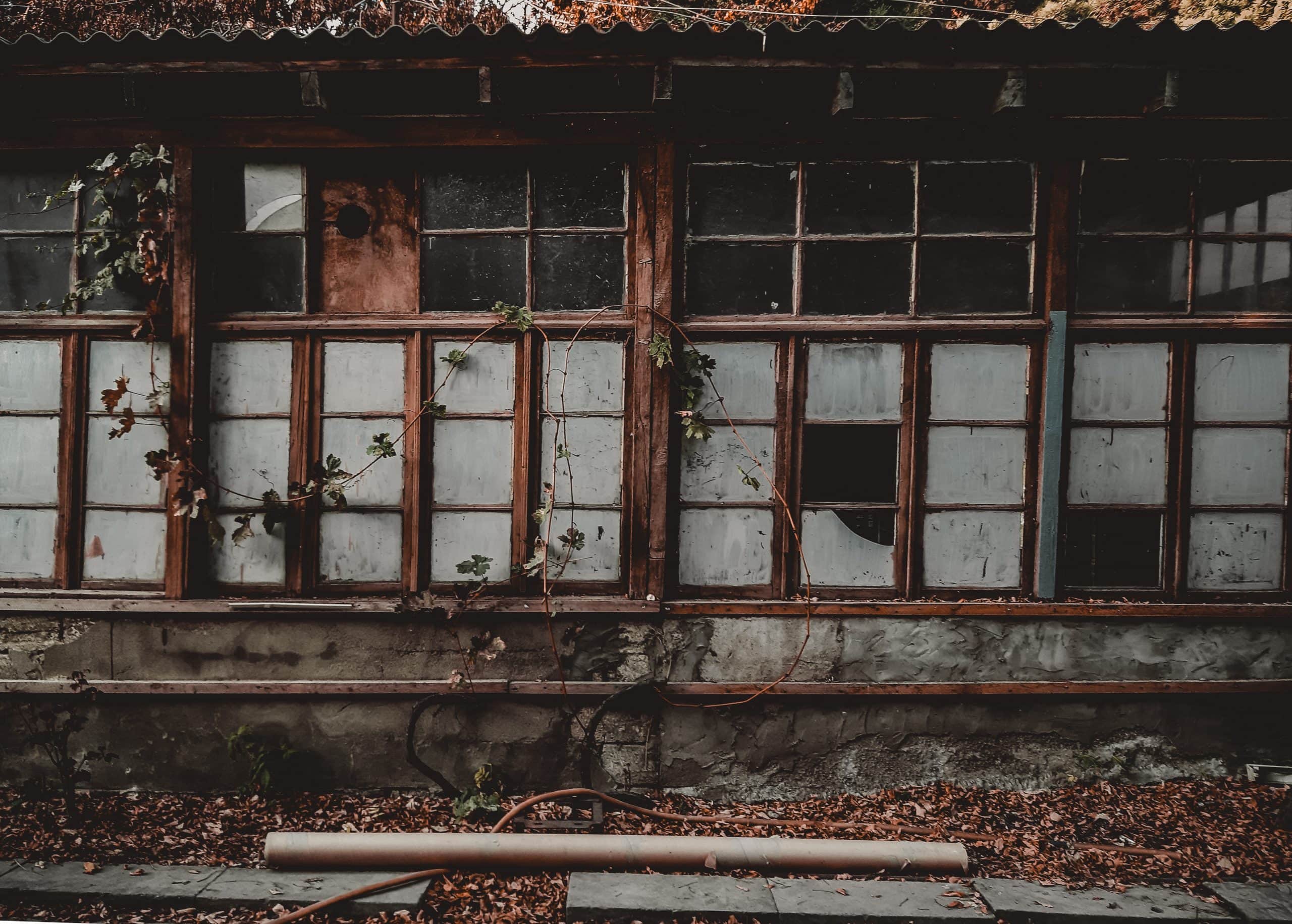

When it comes to patching up damaged wood, there are two main types of materials typically used. Products in these classes include wood fillers and wood repair tools and kits.
Wood Fillers
These are some common types of wood fillers: They dry quickly, require little effort to apply, and show no signs of shrinking after curing. However, in applications that place them outside, they will shrink slightly and may start to peel away from the borders of the wood due to the effects of the weather.
Despite their widespread use, the outcomes from such products aren't usually ideal or very long-lasting. But they serve a useful purpose; for instance, you may use them to make temporary adjustments, and they work wonderfully for straightforward endeavours like fixing nail holes and the like.
Wood Restoration
It's best to use a wood restoration product or kit if your project is large and you want it to seem professional. These are useful for any task requiring wood filler, however using them to plug nail holes would be excessive. Use it to fix up some logs, floorboards, or columns. These items are commonly used to fix rotten window frames.
How to Check for Rotted Wood
If you want to check for rot in the wood, you should take a stroll around your house at least once every few months.
- Take a good look at the trim's edges, particularly where it connects to the floor or the roof.
- Check out window sills as well as other flat wood features that can collect water.
- If you're not sure if a spot is rotten, you can test it by pushing on it with a little screwdriver; if it sinks through and the wood is soft, you've found rot.
Let's discuss the causes, the preventative measures, and the potential solutions for fixing this.
What Causes Wood Rot?
To begin, there are several causes of wood rot, the primary ones being poor wood quality and sloppy construction.
Wood Quality
Since about 1995, "finger-jointed" pine wood has been the standard for trim in most tract homes. This cheap moulding generally breaks after only a few years. Short pieces of wood are cemented together to form a finger-jointed wood trim. Finally, the wood is machined and primed so that it looks wonderful from the very first day it's in place.
When the end grain of the wood becomes wet, or if the paint layer fails, the wood quickly rots because of the porous finger joints. Pinewood, the wood from pine trees that have been artificially cultivated, is softer and less dense than regular wood. The wood from an old-growth pine tree is much denser and more long-lasting than that of a younger tree.
Improper Installation
Mistakes during assembly, such as failing to prime or paint the wood before assembly, are another common source of rot. These tips quickly decay when exposed to the humidity of a home or apartment.
What happens if you put trim wood on a roof without sealing the ends? Wooden moulding will deteriorate if exposed to roof water. The same applies to wood that is resting on the ground or is being pushed up against brick or stone. The wood rots after absorbing water from the masonry, which acts like a sponge.
Fixing Rotten Wood on a Roof
Roof decking, also called sheathing, should be replaced if it is rotten in order to ensure that the entire roof, or even just the damaged piece, remains watertight. Roof decking, which is nailed to the roof's trusses, not only holds roofing materials like shingles and felt paper, but also shields your property from the wind and gives it greater rigidity. If you have any rotten boards on your roof, replacing them can help prevent leaks and water damage to your property. Check out our range of timber repairs Melbourne at Hitch Property Constructions.
Observe the Roof for Signs of Dry Rot
It is important to assess the full extent of the damage and pinpoint its position if you plan to replace only the affected area of the roof. Look around the inside of your house for any holes or cracks. If it has been raining, look for discoloured drywall or wood in the attic, crawl space, and upper floors of the house.
It may be required to take down some walls and some insulation in order to pinpoint the source of water stains on the roof's decking. When replacing a roof, it's important to check the decking after removing the shingles and underlayment. Tap on the water-stained areas with a hammer to ensure they are still solid.
Remove the Shingles
Take off the surrounding shingles that aren't damaged. Each shingle is usually fastened with eight nails: four through the tabs at the top, and four through the shingle directly above it. You may get rid of the felt paper that's stuck under your shingles by simply pulling it up.
As you climb to the top, expose whatever rotting wood you find. The stability of the next row of shingles can be preserved by carefully extracting the second set of four nails. Removing old shingles from a roof requires starting at the peak and working your way down with a pitchfork. Take off all of the roof shingles.
Remove the Rotten Wood
You must first remove the deteriorated decking from the roof before installing the new one. To ensure that all the rotting wood is removed and that enough of the trusses are exposed, you may need to make some extra cuts. The depth setting on your circular saw should be modified to accommodate the roof decking. Take out all of the ruined tissue.
Take the severed section off by prying out the nails with a claw hammer or a pry bar. At least two trusses will need to be exposed so that the replacement wood can be nailed to them for stability. If at all feasible, you should save the removed area intact so that you may accurately measure and cut the replacement.
Replace the Roof Decking
If you're replacing old wood with oriented strand board or plywood, pick a thickness that's similar to the original. If the removed portion was able to be preserved whole, measure its dimensions. If not, you'll have to get on the roof and measure the opening before cutting the replacement to fit.
Cut a piece of replacement material to the correct dimensions and ensure the grain runs perpendicular to the roof trusses. Nail the section to the trusses at regular intervals of 4 to 6 inches once it has been inserted through the aperture.
Replace Underlayment and Shingles
After patching up the plywood roof leak, you should have the seams sealed and a new roof installed. Repair any cracks in the deck with bitumen tape. Apply felt paper to the ceiling with overlaps. Attach it to the roof decking using staples or nails.
Put back the shingles that were taken off. Slide new shingles under the upper course. Nail it to the floor through the one above it, then through its centre. To finish the fix, simply repeat the steps. Stopping leaks and protecting your roof from future damage is as simple as replacing rotten wood. By replacing the entire roof or just a small portion, you may make the roof last much longer.
Wood Rot Prevention
Proper Installation
Never let wood lay directly on brick or soil without first installing flashing or an air space between the two. Pre-installed priming and painting on all six sides.
The colour must reach the other side of the wood. If it isn't, then rain and humidity from inside the home will seep into the wood through the front and rear. It's possible you're already familiar with the term "back-priming," which refers to the practise of priming the component's back in preparation for its installation.
Preventative Maintenance
Regular preventative maintenance is another way to protect a building from wood rot. Once every three to seven years, depending on the quality of the wood, you should clean, caulk, and repaint the trim. Failure to regularly paint the wood will result in the paint flaking off, exposing the wood to the environment and increasing its susceptibility to moisture absorption.
Repairing Rotted Wood
Let's discuss the options for short-term, medium-term, and permanent solutions to the problem of rotting wood.
The Quick Fix
The rotten piece should be dug out, allowed to dry, filled with epoxy, primed, and then painted. When the rotten region is dry enough to take the filler, this repair is a suitable option if you're on a budget or if replacing the rotted section is difficult. You can also use wood filler if you choose. Epoxy is much more durable than external wood filler, which is porous and will rot in a year.
General maintenance and fixes can be done with pine. The worst type of wood is finger-jointed wood, whereas the greatest type of wood is clear pine. A new piece of wood could be installed once the old one is removed, primed, and painted. It's likely to rot again.
We have a wide range of Melbourne timber repairs for your home renovations. Check out Hitch Property Constructions.
FAQs About Wood Rot
Some find painting rotten wood a quick and easy fix. However, it only hides the rot and makes the wood visually appealing. It ignores the underlying causes that can lead to severe issues down the line. Painting does not stop wood deterioration; it simply delays the process of the wood falling apart.
The common type of wood rot you may encounter and what is often confused with termite damage is dry rot. Dry rot is caused by fungi that attack wood and destroys its interior structure, hollowing it out from the inside.
'Dry rot' is an 18th-century term that generally described what is now called brown rot. The term was used because the damage was present in cured or dried timber of ships and buildings and was thought to be caused by internal 'fermentations' rather than water.
Sand the damaged area with medium-grit sandpaper, following the direction of the wood grain. The goals are to smooth the wood, remove loose paint, and prepare the surface for accepting new primer and paint.
Can Rotten Wood Be Repaired? Rotting wood can be repaired by first removing any rot from the original board or beam of wood. Once that has been done, you can fill the area with a wood-patch or polyester filler. This material will fill the area and harden to provide strength and durability.
Conclusion
The wooden mouldings in the home are probably affected by wood rot. Not all wood needs to be replaced unless it's rotten or otherwise dangerous to the structure. The fix won't hold unless both the rotten and healthy wood are replaced. Wood fillers and repair tools and kits are the two most common ways to fix broken wood. Rotten boards on a roof can cause leaks and expensive repairs if they are not replaced.
When using a pitchfork to remove old shingles from a roof, it is best to begin at the highest point and work your way down. Deteriorated roof decking must be removed before new decking can be installed. The replacement material you use must fit precisely into the hole, so be sure to measure first. A leaking roof can be fixed by simply replacing the shingles and underlayment. Depending on the extent of the damage, a new roof could extend the life of your building significantly. Flashing or an air gap should always be installed before laying wood on brick or soil.
Content Summary
- Wood rot is likely affecting the house's wooden mouldings.
- Any wood in a house is susceptible to wet or dry rot.
- Warning signs include wood that has rotted at the door, trim, window sill, floor, window sill, or column.
- The bad news is that replacing damaged wood is a pain and can be quite costly.
- Wood that isn't supporting the building almost never needs to be replaced.
- To fortify the vulnerable spot, try using simple products.
- Both the rotted and unrotted wood must be repaired for the fix to last.
- When it comes to patching up damaged wood, there are two main types of materials typically used.
- Products in these classes include wood fillers and wood repair tools and kits.
- It's best to use a wood restoration product or kit if your project is large and you want it to seem professional.
- Use it to fix up some logs, floorboards, or columns.
- If you're not sure if a spot is rotten, you can test it by pushing on it with a little screwdriver; if it sinks through and the wood is soft, you've found rot.
- Short pieces of wood are cemented together to form a finger-jointed wood trim.
- What happens if you put trim wood on a roof without sealing the ends?
- Roof decking, also called sheathing, should be replaced if it is rotten in order to ensure that the entire roof, or even just the damaged piece, remains watertight.
- Look around the inside of your house for any holes or cracks.
- It may be required to take down some walls and some insulation in order to pinpoint the source of water stains on the roof's decking.
- When replacing a roof, it's important to check the decking after removing the shingles and underlayment.
- Take off the surrounding shingles that aren't damaged.
- Take off all of the roof shingles.
- You must first remove the deteriorated decking from the roof before installing the new one.
- To ensure that all the rotting wood is removed and that enough of the trusses are exposed, you may need to make some extra cuts.
- Take out all of the ruined tissue.
- If you're replacing old wood with oriented strand board or plywood, pick a thickness that's similar to the original.
- Nail the section to the trusses at regular intervals of 4 to 6 inches once it has been inserted through the aperture.
- After patching up the plywood roof leak, you should have the seams sealed and a new roof installed.
- Repair any cracks in the deck with bitumen tape.
- Apply felt paper to the ceiling with overlaps.
- Attach it to the roof decking using staples or nails.
- Slide new shingles under the upper course.
- Stopping leaks and protecting your roof from future damage is as simple as replacing rotten wood.
- By replacing the entire roof or just a small portion, you may make the roof last much longer.
- Pre-installed priming and painting on all six sides.
- The colour must reach the other side of the wood.
- It's possible you're already familiar with the term "back-priming," which refers to the practise of priming the component's back in preparation for its installation.
- Regular preventative maintenance is another way to protect a building from wood rot.
- Once every three to seven years, depending on the quality of the wood, you should clean, caulk, and repaint the trim.
- When the rotten region is dry enough to take the filler, this repair is a suitable option if you're on a budget or if replacing the rotted section is difficult.
- You can also use wood filler if you choose.
- General maintenance and fixes can be done with pine.
- A new piece of wood could be installed once the old one is removed, primed, and painted.